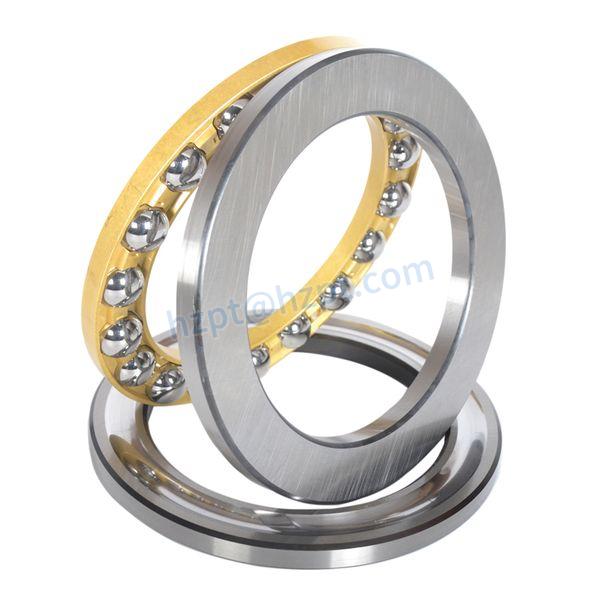
Product Description
Product Parameters
| Model | Category | RTS/Custom | Size(mm) d*D*H (mm) |
Precision grade | Seal Type | Number of Row | Application |
| 6009 | Deep Groove Ball Bearing | RTS | 45*75*16mm | P0 P2 P4 P5 P6 | OPEN ZZ 2RS RS | Single | Machinery |
| Material | Material of Balls | Lubrication | Vibration | Clearance | Hardness | Deliery Time | Packing |
| Chrome Steel GCr15 | Chrome Steel GCr15 | Grease or Oil | Standard Vibration | Standard Clearance | HRC60-65 | <=50000,3 <=100000,5 |
Single Box+Cartons+Pallet |
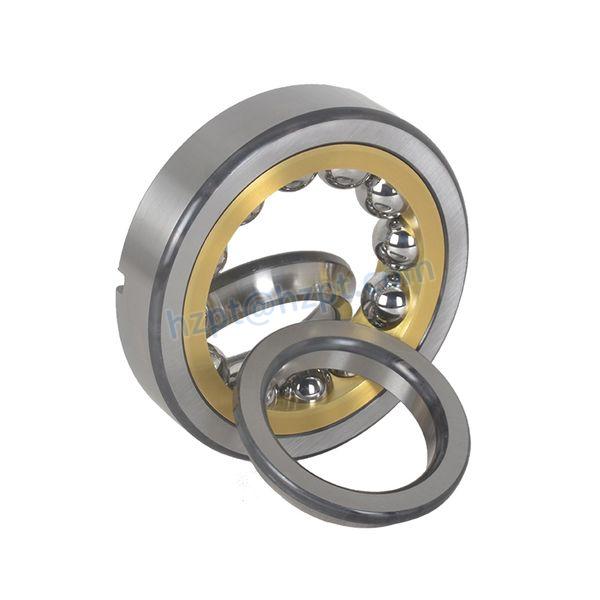
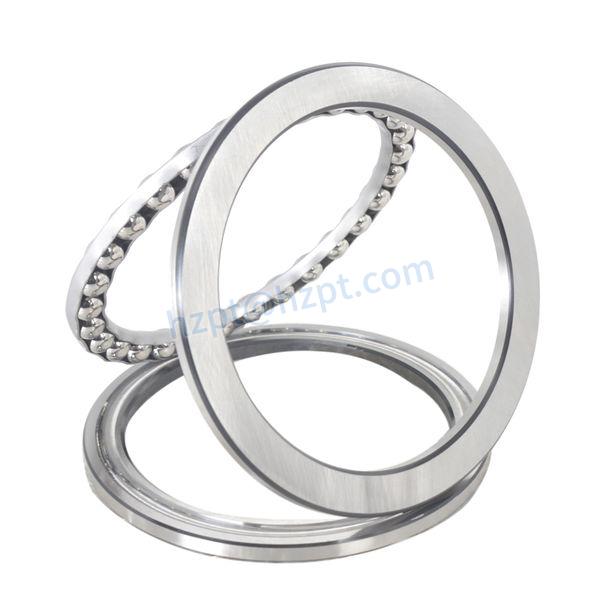
Product Description
Detailed Photos
Our business:Produce and customize various bearing brands. (Packaging and logo can be customized. All copyright belongs to the customer. We promise not to disclose any information.)
Product Series
| Bearing type | Boundary Dimensions( mm ) | Speed Rating(ipm) | Load Rating(kn) | Weight(kg) | ||||
| d | D | B | Grease lubrication | Oil lubrication | Dynamic Cr | Static Cor | ||
| 6000 | 10 | 26 | 8 | 22000 | 30000 | 4.55 | 1.97 | 0.019 |
| 6001 | 12 | 28 | 8 | 20000 | 26000 | 5.1 | 2.38 | 0.571 |
| 6002 | 15 | 32 | 9 | 19000 | 24000 | 5.58 | 2.85 | 0.03 |
| 6003 | 17 | 35 | 10 | 17000 | 21000 | 6 | 3.25 | 0.04 |
| 6004 | 20 | 42 | 12 | 16000 | 19000 | 9.38 | 5.02 | 0.069 |
| 6005 | 25 | 47 | 12 | 15000 | 18000 | 10.1 | 5.85 | 0.08 |
| 6006 | 30 | 55 | 13 | 13000 | 15000 | 13.2 | 8.3 | 0.116 |
| 6007 | 35 | 62 | 14 | 11000 | 13000 | 16 | 10.3 | 0.155 |
| 6008 | 40 | 68 | 15 | 9000 | 11000 | 17 | 11.8 | 0.185 |
| 6009 | 45 | 75 | 16 | 8000 | 10000 | 21 | 14.8 | 0.23 |
| 6571 | 50 | 80 | 16 | 7000 | 9000 | 22.05 | 16.21 | 0.25 |
| 6011 | 55 | 90 | 18 | 7000 | 8500 | 30.2 | 21.8 | 0.362 |
| 6012 | 60 | 95 | 18 | 6300 | 7500 | 31.65 | 24.22 | 0.385 |
| 6013 | 65 | 100 | 18 | 6000 | 7000 | 32 | 24.72 | 0.41 |
| 6014 | 70 | 110 | 20 | 5000 | 6700 | 38.5 | 30.5 | 0.575 |
| 6015 | 75 | 115 | 20 | 5300 | 6300 | 40.2 | 33.2 | 0.603 |
| 6016 | 80 | 125 | 22 | 5000 | 6000 | 47.5 | 39.8 | 0.821 |
| 6017 | 85 | 130 | 22 | 4500 | 5600 | 50.8 | 42.8 | 0.848 |
| 6018 | 90 | 140 | 24 | 4300 | 5300 | 58 | 49.8 | 1.1 |
| 6019 | 95 | 145 | 24 | 4000 | 5000 | 57.8 | 50 | 1.15 |
| 6571 | 100 | 150 | 24 | 3800 | 4800 | 64.5 | 56.2 | 1.18 |
| 6571 | 110 | 170 | 28 | 3400 | 4300 | 81.8 | 72.8 | 1.89 |
| 6571 | 120 | 180 | 28 | 3000 | 3800 | 87.5 | 79.2 | 1.99 |
| 6026 | 130 | 200 | 33 | 2800 | 3600 | 105 | 96.8 | 3.08 |
| 6571 | 140 | 210 | 33 | 2400 | 3200 | 116 | 108 | 3.17 |
| 6030 | 150 | 225 | 35 | 2200 | 3000 | 132 | 125 | 3.9 |
| 6032 | 160 | 240 | 38 | 2000 | 2800 | 145 | 138 | 4.83 |
| 6034 | 170 | 260 | 42 | 1900 | 2600 | 170 | 170 | 6.5 |
| 6036 | 180 | 280 | 46 | 1300 | 2400 | 188 | 198 | 8.51 |
| 6038 | 190 | 290 | 46 | 1700 | 2200 | 188 | 200 | 8.865 |
| 6040 | 200 | 310 | 51 | 1600 | 2000 | 205 | 225 | 11.64 |
| 6044 | 220 | 340 | 56 | 1400 | 1800 | 252 | 268 | 18 |
| 6048 | 240 | 360 | 56 | 1200 | 1600 | 270 | 292 | 20 |
| 6052 | 260 | 400 | 65 | 1100 | 1500 | 292 | 372 | 28.8 |
| 6056 | 280 | 420 | 65 | 950 | 1300 | 305 | 408 | 32.1 |
| 6060 | 300 | 460 | 74 | 930 | 1200 | 358 | 500 | 42.8 |
| 6064 | 320 | 480 | 74 | 900 | 1100 | 345 | 513 | 48.4 |
| 6068 | 340 | 520 | 82 | 800 | 1000 | 423 | 640 | 67.2 |
| 6072 | 360 | 540 | 82 | 750 | 950 | 400 | 622 | 68 |
| 6076 | 380 | 560 | 82 | 700 | 900 | 436 | 695 | 75 |
| 6080 | 400 | 600 | 90 | 680 | 800 | 512 | 868 | 89.4 |
| 6084 | 420 | 620 | 90 | 630 | 750 | 507 | 880 | 98 |
| 6088 | 440 | 650 | 94 | 600 | 700 | 553 | 965 | 107 |
| 6092 | 460 | 680 | 100 | 580 | 640 | 592 | 1060 | 130 |
| 6096 | 480 | 700 | 100 | 550 | 610 | 618 | 1140 | 132 |
| 60/500 | 500 | 720 | 100 | 520 | 580 | 415 | 1571 | 135 |
| 60/530 | 530 | 780 | 112 | 490 | 530 | 650 | 1270 | 186 |
| 60/560 | 560 | 820 | 115 | 460 | 510 | 663 | 1370 | 208 |
| 60/600 | 600 | 870 | 118 | 420 | 470 | 728 | 1500 | 257 |
| 60/630 | 630 | 920 | 128 | 400 | 430 | 819 | 1760 | 303 |
| 60/670 | 670 | 980 | 136 | 370 | 370 | 904 | 2040 | 348 |
| 60/710 | 710 | 1030 | 140 | 340 | 350 | 956 | 2200 | 390 |
| 60/750 | 750 | 1090 | 150 | 310 | 310 | 995 | 2360 | 420 |
| 60/800 | 800 | 1150 | 155 | 290 | 290 | 1571 | 2550 | 470 |
| 60/850 | 850 | 1220 | 650 | 260 | 240 | 1120 | 2900 | 503 |
| 60/900 | 900 | 1280 | 170 | 230 | 220 | 1140 | 3100 | 579 |
| 60/1000 | 1000 | 1420 | 185 | 200 | 180 | 1350 | 3900 | 602 |
| 60/1060 | 1060 | 1500 | 195 | 190 | 140 | 1530 | 4500 | 636 |
| 60/1120 | 1120 | 1580 | 200 | 140 | 100 | 1460 | 4400 | 690 |
Type Of Deep Groove Ball Bearing
1. Deep Groove Ball Bearing With Dust Cover
Generally Used In The Single Lubrication Is More Difficult, The Placement Of Lubricating Oil And Check The Lubrication Is Not Convenient Conditions, Usually Injected Into The Bearing Rust, Lubrication Dual-Purpose Lithium Grease Is 1/4 To 1/3 Of The Bearing Internal Space.
2. Deep Groove Ball Bearing With Sealing Ring
Its Performance, Grease Filling, Use And Bearing With Dust Cover Are Basically The Same, The Difference Is That There Is A Large Gap Between The Dust Cover And The Inner Ring, And The Sealing Lip And The Inner Ring Of The Non-Contact Seal Ring Is Small, There Is No Gap Between The Sealing Lip And The Inner Ring Of The Contact Seal Ring Bearing, The Sealing Effect Is Good, But The Friction Coefficient Has Increased.
3, There Are Stop Groove And Deep Groove Ball Bearings With Stop Ring
In Addition To The Function Of Bearing Radial Load, The Deep Groove Ball Bearing With The Stop Ring Can Also Limit The Axial Displacement Of The Bearing, Simplify The Structure Of The Bearing Seat And Reduce The Bearing Size. Generally Used In Cars, Tractors And Other Axial Load Is Not Large Working Parts.
4. Deep Groove Ball Bearing With Ball Filling Gap
There Are Notches In The Inner And Outer Rings On One Side, From Which More Balls Can Be Loaded, Increasing Its Radial Load Capacity. However, Due To The Small Axial Load Capacity, It Can Not Run At High Speed. If There Is A Large Axial Load, It Needs To Be Used With The General Deep Groove Ball Bearing.
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
Exhibitions&Partners
FAQ
Q:Are you trading company or manufacturer?
–We are the company dealing in trading business and manufacturing business.
Q:What’s the MOQ?
–MOQ is 2pcs for standardized products; 300pcs for customized products. There is no MOQ for sample orders.
Q:How long is the lead time?
–The lead time for sample orders is 1-3 days, for bulk orders is generally in 3-15 days.The delivery time is generally in 2 days after payment. It’s according to the order amount.
Q:Do you offer free samples?
–If you place an order, we can return part of sample fee even all of fee to you. It also depends on the quantity of order and the type of sample. And you just need to pay freight.
Q: Could you customized for me?
–Sure,we can supply OEM service as per your drawing or samples.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Chrome Steel Gcr15 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 0.23kg |
| Transport Package: | Single Box+Cartons+Pallet |
| Specification: | 45*75*16mm |
| Origin: | China |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can you Provide Examples of Industries where Ball Bearings are Crucial Components?
Ball bearings are essential components in a wide range of industries where smooth motion, load support, and precision are vital. Here are some examples of industries where ball bearings play a crucial role:
- Automotive Industry:
Ball bearings are used in various automotive applications, including wheel hubs, transmissions, engines, steering systems, and suspension components. They provide reliable rotation and support in both passenger vehicles and commercial vehicles.
- Aerospace Industry:
In the aerospace sector, ball bearings are found in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, control surfaces, and avionics equipment. Their ability to handle high speeds and precision is vital for aviation safety.
- Industrial Machinery:
Ball bearings are integral to a wide range of industrial machinery, including pumps, compressors, conveyors, machine tools, printing presses, and textile machinery. They facilitate smooth operation and load distribution in these diverse applications.
- Medical Equipment:
In medical devices and equipment, ball bearings are used in surgical instruments, imaging equipment, dental tools, and laboratory machinery. Their precision and smooth movement are crucial for accurate diagnostics and treatments.
- Robotics and Automation:
Ball bearings are key components in robotic arms, automation systems, and manufacturing machinery. They enable precise movement, high-speed operation, and reliable performance in automated processes.
- Renewable Energy:
Wind turbines and solar tracking systems utilize ball bearings to enable efficient rotation and tracking of the wind blades and solar panels. Ball bearings withstand the dynamic loads and environmental conditions in renewable energy applications.
- Marine and Shipbuilding:
Ball bearings are used in marine applications such as ship propulsion systems, steering mechanisms, and marine pumps. They withstand the corrosive environment and provide reliable performance in maritime operations.
- Heavy Equipment and Construction:
In construction machinery like excavators, bulldozers, and cranes, ball bearings support the movement of heavy loads and enable efficient operation in demanding environments.
- Electronics and Consumer Appliances:
Consumer electronics like electric motors, computer hard drives, and household appliances rely on ball bearings for smooth motion and reliable operation.
- Oil and Gas Industry:
In oil and gas exploration and extraction equipment, ball bearings are used in drilling rigs, pumps, and processing machinery. They handle the high loads and harsh conditions of this industry.
These examples demonstrate how ball bearings are indispensable components in various industries, contributing to the efficiency, reliability, and functionality of diverse mechanical systems and equipment.

How do Temperature and Environmental Conditions Affect the Performance of Ball Bearings?
Temperature and environmental conditions have a significant impact on the performance and longevity of ball bearings. The operating environment can influence factors such as lubrication effectiveness, material properties, and overall bearing behavior. Here’s how temperature and environmental conditions affect ball bearing performance:
- Lubrication:
Temperature variations can affect the viscosity and flow characteristics of lubricants. Extreme temperatures can cause lubricants to become too thin or too thick, leading to inadequate lubrication and increased friction. In high-temperature environments, lubricants can degrade, reducing their effectiveness.
- Material Properties:
Temperature changes can alter the material properties of the bearing components. High temperatures can lead to thermal expansion, affecting bearing clearances and potentially causing interference between components. Extreme cold temperatures can make materials more brittle and prone to fracture.
- Clearance Changes:
Temperature fluctuations can cause changes in the internal clearance of ball bearings. For instance, at high temperatures, materials expand, leading to increased clearance. This can affect bearing performance, load distribution, and overall stability.
- Corrosion and Contamination:
Harsh environmental conditions, such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or abrasive particles, can lead to corrosion and contamination of bearing components. Corrosion weakens the material, while contamination accelerates wear and reduces bearing life.
- Thermal Stress:
Rapid temperature changes can result in thermal stress within the bearing components. Differential expansion and contraction between the inner and outer rings can lead to stress and distortion, affecting precision and bearing integrity.
- Noise and Vibration:
Temperature-related changes in material properties and internal clearances can influence noise and vibration levels. Extreme temperatures can lead to increased noise generation and vibration, affecting the overall operation of machinery.
- Lubricant Degradation:
Environmental factors like humidity, dust, and contaminants can lead to premature lubricant degradation. Oxidation, moisture absorption, and the presence of foreign particles can compromise the lubricant’s performance and contribute to increased friction and wear.
- Seal Effectiveness:
Seals and shields that protect bearings from contaminants can be affected by temperature fluctuations. Extreme temperatures can lead to seal hardening, cracking, or deformation, compromising their effectiveness in preventing contamination.
- Choosing Appropriate Bearings:
When selecting ball bearings for specific applications, engineers must consider the expected temperature and environmental conditions. High-temperature bearings, bearings with specialized coatings, and those with enhanced sealing mechanisms may be necessary to ensure reliable performance.
Overall, understanding the impact of temperature and environmental conditions on ball bearing performance is crucial for proper bearing selection, maintenance, and ensuring optimal operation in diverse industries and applications.

How do Ball Bearings Differ from Other Types of Bearings like Roller Bearings?
Ball bearings and roller bearings are two common types of rolling-element bearings, each with distinct designs and characteristics. Here’s a comparison of ball bearings and roller bearings:
- Design:
Ball Bearings: Ball bearings use spherical balls to separate and reduce friction between the bearing’s inner and outer rings. The balls enable rolling motion and smooth contact, minimizing friction.
Roller Bearings: Roller bearings, as the name suggests, use cylindrical or tapered rollers instead of balls. These rollers have larger contact areas, distributing loads over a broader surface.
- Friction and Efficiency:
Ball Bearings: Due to the point contact between the balls and the rings, ball bearings have lower friction and are more efficient at high speeds.
Roller Bearings: Roller bearings have a larger contact area, resulting in slightly higher friction compared to ball bearings. They are more suitable for heavy-load applications where efficiency is prioritized over high speeds.
- Load Capacity:
Ball Bearings: Ball bearings excel at handling light to moderate loads in both radial and axial directions. They are commonly used in applications where smooth rotation and low friction are important.
Roller Bearings: Roller bearings have a higher load-carrying capacity than ball bearings. They can support heavier radial and axial loads and are preferred for applications with significant loads or impact forces.
- Variability:
Ball Bearings: Ball bearings come in various designs, including deep groove, angular contact, and thrust ball bearings, each suitable for different applications.
Roller Bearings: Roller bearings have diverse types, including cylindrical, spherical, tapered, and needle roller bearings, each optimized for specific load and motion requirements.
- Speed Capability:
Ball Bearings: The reduced friction in ball bearings makes them suitable for high-speed applications, such as electric motors and precision machinery.
Roller Bearings: Roller bearings can handle higher loads but are generally better suited for moderate to low speeds due to slightly higher friction.
- Applications:
Ball Bearings: Ball bearings are used in applications where smooth motion, low friction, and moderate loads are essential, such as electric fans, bicycles, and some automotive components.
Roller Bearings: Roller bearings find applications in heavy machinery, construction equipment, automotive transmissions, and conveyor systems, where heavier loads and durability are crucial.
In summary, ball bearings and roller bearings differ in their design, friction characteristics, load capacities, speed capabilities, and applications. The choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the machinery and the type of loads and forces involved.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China Professional Deep Groove Ball Bearing/16011/Nskskf/Necessary Accessories for Mechanical Equipment Rotation deep groove ball bearing
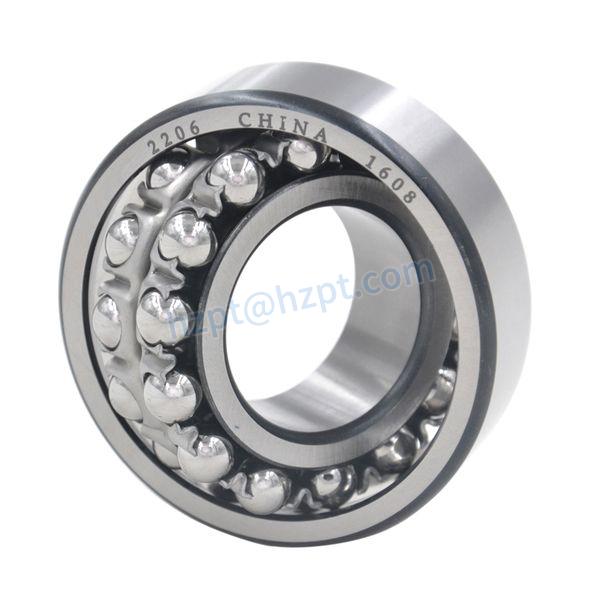
Product Description
Deep Groove Ball Bearing/16011/Nskskf/Rolling Bearing/Necessary accessories for mechanical equipment rotation
Product Description
1. Model: CZPT 16011
2. Type: Deep Groove Ball Bearing
– Deep groove ball bearings are 1 of the most common types of bearings, known for their high load-carrying capacity and smooth operation.
– They are suitable for various applications, including power tools, automotive components, machinery, etc.
3. Dimensional Parameters:
– Inner Diameter (d): 55 millimeters
– Outer Diameter (D):90 millimeters
– Width (B): 11 millimeters
4. Material:
– The inner and outer rings, as well as the rolling elements, are typically made of high-quality bearing steel to provide sufficient strength and wear resistance.
| Model | Dust cover type | Sealing ring type | Bore Diameter (mm) | Outer Diameter(mm) | Width(mm) |
| 6810 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 50 | 65 | 7 |
| 6910 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 50 | 72 | 12 |
| 16571 | – | – | 50 | 80 | 10 |
| 6571 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 50 | 80 | 16 |
| 6210 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 50 | 90 | 20 |
| 6310 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 50 | 110 | 27 |
| 6811 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 55 | 72 | 9 |
| 6911 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 55 | 80 | 13 |
| 16011 | – | – | 55 | 90 | 11 |
| 6011 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 55 | 90 | 18 |
| 6211 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 55 | 100 | 21 |
| 6311 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 55 | 120 | 29 |
| 6812 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 60 | 78 | 10 |
| 6912 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 60 | 85 | 13 |
| 16012 | – | – | 60 | 95 | 11 |
| 6012 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 60 | 95 | 18 |
| 6212 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 60 | 110 | 22 |
| 6312 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 60 | 130 | 31 |
| 6813 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 65 | 85 | 10 |
| 6913 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 65 | 90 | 13 |
| 16013 | – | – | 65 | 100 | 11 |
| 6013 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 65 | 100 | 18 |
| 6213 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 65 | 120 | 23 |
| 6313 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 65 | 140 | 33 |
| 6814 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 70 | 90 | 10 |
| 6914 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 70 | 100 | 16 |
| 16014 | – | – | 70 | 110 | 13 |
| 6014 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 70 | 110 | 20 |
| 6214 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 70 | 125 | 24 |
| 6314 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 70 | 150 | 35 |
| 6815 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 75 | 95 | 10 |
| 6915 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 75 | 105 | 16 |
| 16015 | – | – | 75 | 115 | 13 |
| 6015 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 75 | 115 | 20 |
| 6215 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 75 | 130 | 25 |
| 6315 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 75 | 160 | 37 |
| 6816 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 80 | 100 | 10 |
| 6916 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 80 | 110 | 16 |
| 16016 | – | – | 80 | 125 | 14 |
| 6016 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 80 | 125 | 22 |
| 6216 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 80 | 140 | 26 |
| 6316 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 80 | 170 | 39 |
| 6817 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 85 | 110 | 13 |
| 6917 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 85 | 120 | 18 |
| 16017 | – | – | 85 | 130 | 14 |
| 6017 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 85 | 130 | 22 |
| 6217 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 85 | 150 | 28 |
| 6317 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 85 | 180 | 41 |
| 6818 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 90 | 115 | 13 |
| 6918 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 90 | 125 | 18 |
| 16018 | – | – | 90 | 140 | 16 |
| 6018 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 90 | 140 | 24 |
| 6218 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 90 | 160 | 30 |
| 6318 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 90 | 190 | 43 |
| 6819 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 95 | 120 | 13 |
| 6919 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 95 | 130 | 18 |
| 16019 | – | – | 95 | 145 | 16 |
| 6019 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 95 | 145 | 24 |
| 6219 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 95 | 170 | 32 |
| 6319 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 95 | 200 | 45 |
| 6820 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 100 | 125 | 13 |
| 6920 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 100 | 140 | 20 |
| 16571 | – | – | 100 | 150 | 16 |
| 6571 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 100 | 150 | 24 |
| 6220 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 100 | 180 | 34 |
| 6320 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 100 | 215 | 47 |
| 6821 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 105 | 130 | 13 |
| 6921 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 105 | 145 | 20 |
| 16571 | – | – | 105 | 160 | 18 |
| 6571 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 105 | 160 | 26 |
| 6221 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 105 | 190 | 36 |
| 6321 | ZZ | VV/DD/DDU | 105 | 225 | 49 |
Applications of Deep Groove Ball Bearings:
Deep groove ball bearings are a common type of bearing with a wide range of applications. Here are some common applications of deep groove ball bearings:
1. Electric Motors and Engines: Deep groove ball bearings are commonly used in electric motors and engines to support the rotating motion of the rotor and withstand axial and radial loads.
2. Automotive Industry: Deep groove ball bearings are widely used in the automotive industry, including engine, transmission systems, suspension systems, wheels, and subframes.
3. Machinery Equipment: Deep groove ball bearings are suitable for various machinery equipment, such as industrial machinery, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, textile machinery, etc. They are used for power transmission, supporting rotating components, and reducing friction.
4. Pumps and Fans: Deep groove ball bearings are used in rotating equipment such as pumps and fans to support the rotation of the impeller and provide stable operation.
5. Household Appliances: Deep groove ball bearings are commonly found in household appliances such as washing machines, air conditioners, electric fans, etc., to support the rotation of motor rotors.
6. Industrial Transmissions: Deep groove ball bearings are used in various industrial transmission systems, such as gear transmissions, chain drives, etc., to support rotational motion and transmit torque.
7. Bicycles and Motorcycles: Deep groove ball bearings are widely used in bicycle and motorcycle wheels, steering systems, and engines.
These are just some common applications of deep groove ball bearings. In reality, deep groove ball bearings are widely used in various machinery and industries. Their simple structure and efficient performance make them an ideal choice for many rotating devices.
Deep groove ball bearings have several advantages:
1. High load-carrying capacity: Deep groove ball bearings can withstand both radial and axial loads, making them suitable for various load conditions.
2. Low friction and high efficiency: Deep groove ball bearings have a ball-and-groove structure, resulting in low frictional losses and providing high speed and operational efficiency.
3. Axial stability: The structure of deep groove ball bearings offers good axial stability, allowing them to withstand axial forces and prevent axial displacement.
4. Simplified installation and maintenance: Deep groove ball bearings have a simple structure, making them easy to install and dismantle, saving time and costs. Additionally, they often do not require additional lubrication or sealing devices.
5. Diverse applications: Deep groove ball bearings are widely used in various industries and fields, including machinery, automotive, power tools, and household appliances, meeting different application requirements.
6. High reliability and durability: Deep groove ball bearings are made of high-quality materials and undergo precision manufacturing, ensuring excellent reliability and durability to maintain stable performance during long-term operation.
In summary, deep groove ball bearings offer advantages such as high load-carrying capacity, low friction and high efficiency, axial stability, simplified installation and maintenance, diverse applications, and high reliability and durability. These characteristics make them a crucial type of bearing widely used in various industrial
FAQ
1.What is the minimum order quantity for this product?
Can be negotiated, we will try our best to meet customer needs.Our company is mainly based on wholesale sales, most customers’orders are more than Over 500 sets.
2.What is your latest delivery time?
Most orders will be shipped within 3-5 days of payment being received.
3.Does your company have quality assurance?
Yes, for 1 years.
4.Are you a factory or a trading company?
We have our own cooperative factory, and our business type is a combination of manufacturing and trading.
5.What is the competitiveness of your company’s products compared to other companies?
High precision, high speed, low noise.
6.What are the advantages of your company’s services compared to other companies?
Answer questions online 24 hours a day, reply in a timely manner, 100% after-sales service.
7.Which payment method does your company support?
Do our best to meet customer needs, Can be negotiated.
8.How to contact us quickly?
Please send us an inquiry or message and leave your other contact information, we will contact you as soon as possible and provide the detailed information you need.
Product inventory display
Company strength display
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Separated: | Unseparated |
|---|---|
| Rows Number: | Single |
| Load Direction: | Radial Bearing |
| Material: | Bearing Steel |
| Contact Angle: | 0 |
| Aligning: | 0 |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the Common Signs of Wear or Damage in Ball Bearings that Indicate the Need for Replacement?
Ball bearings are subjected to wear and stress during operation, and over time, they may exhibit signs of damage or deterioration that warrant replacement. Recognizing these signs is crucial to prevent catastrophic failure and ensure safe and reliable operation. Here are the common signs of wear or damage in ball bearings:
- Unusual Noise:
If you hear unusual grinding, clicking, or rumbling noises coming from the bearing during operation, it may indicate worn-out or damaged components. Unusual noise suggests that the bearing is no longer operating smoothly.
- Vibration:
Excessive vibration in the machinery can be a sign of bearing wear. Vibrations can result from uneven wear, misalignment, or damaged components within the bearing.
- Increased Temperature:
Higher operating temperatures than usual may indicate increased friction due to inadequate lubrication, wear, or other issues. Monitoring the bearing’s temperature can help identify potential problems.
- Irregular Movement:
If you notice irregular movement, jerking, or sticking during rotation, it could be a sign that the bearing is no longer operating smoothly. This may be due to damaged rolling elements or raceways.
- Reduced Performance:
If the machinery’s performance has decreased, it may be due to a compromised bearing. Reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, or a decline in overall performance could be indicators of bearing wear.
- Visible Wear or Damage:
Inspect the bearing for visible signs of wear, such as pitting, scoring, or discoloration on the rolling elements or raceways. Severe wear or damage is a clear indication that the bearing needs replacement.
- Leakage or Contamination:
If there is evidence of lubricant leakage, contamination, or the presence of foreign particles around the bearing, it suggests that the seal or shield may be compromised, leading to potential damage.
- Looseness or Excessive Play:
If you can feel excessive play or looseness when manually moving the bearing, it could indicate worn-out components or misalignment.
- Reduced Lifespan:
If the bearing’s expected lifespan is significantly shorter than usual, it may be due to inadequate lubrication, excessive loads, or improper installation, leading to accelerated wear.
- Frequent Failures:
If the bearing is consistently failing despite regular maintenance and proper use, it could indicate a chronic issue that requires addressing, such as inadequate lubrication or misalignment.
It’s important to conduct regular inspections, monitor performance, and address any signs of wear or damage promptly. Replacing worn or damaged ball bearings in a timely manner can prevent further damage to machinery, reduce downtime, and ensure safe and efficient operation.

How do Temperature and Environmental Conditions Affect the Performance of Ball Bearings?
Temperature and environmental conditions have a significant impact on the performance and longevity of ball bearings. The operating environment can influence factors such as lubrication effectiveness, material properties, and overall bearing behavior. Here’s how temperature and environmental conditions affect ball bearing performance:
- Lubrication:
Temperature variations can affect the viscosity and flow characteristics of lubricants. Extreme temperatures can cause lubricants to become too thin or too thick, leading to inadequate lubrication and increased friction. In high-temperature environments, lubricants can degrade, reducing their effectiveness.
- Material Properties:
Temperature changes can alter the material properties of the bearing components. High temperatures can lead to thermal expansion, affecting bearing clearances and potentially causing interference between components. Extreme cold temperatures can make materials more brittle and prone to fracture.
- Clearance Changes:
Temperature fluctuations can cause changes in the internal clearance of ball bearings. For instance, at high temperatures, materials expand, leading to increased clearance. This can affect bearing performance, load distribution, and overall stability.
- Corrosion and Contamination:
Harsh environmental conditions, such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or abrasive particles, can lead to corrosion and contamination of bearing components. Corrosion weakens the material, while contamination accelerates wear and reduces bearing life.
- Thermal Stress:
Rapid temperature changes can result in thermal stress within the bearing components. Differential expansion and contraction between the inner and outer rings can lead to stress and distortion, affecting precision and bearing integrity.
- Noise and Vibration:
Temperature-related changes in material properties and internal clearances can influence noise and vibration levels. Extreme temperatures can lead to increased noise generation and vibration, affecting the overall operation of machinery.
- Lubricant Degradation:
Environmental factors like humidity, dust, and contaminants can lead to premature lubricant degradation. Oxidation, moisture absorption, and the presence of foreign particles can compromise the lubricant’s performance and contribute to increased friction and wear.
- Seal Effectiveness:
Seals and shields that protect bearings from contaminants can be affected by temperature fluctuations. Extreme temperatures can lead to seal hardening, cracking, or deformation, compromising their effectiveness in preventing contamination.
- Choosing Appropriate Bearings:
When selecting ball bearings for specific applications, engineers must consider the expected temperature and environmental conditions. High-temperature bearings, bearings with specialized coatings, and those with enhanced sealing mechanisms may be necessary to ensure reliable performance.
Overall, understanding the impact of temperature and environmental conditions on ball bearing performance is crucial for proper bearing selection, maintenance, and ensuring optimal operation in diverse industries and applications.

What is a Ball Bearing and How does it Function in Various Applications?
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to reduce friction between moving parts and support radial and axial loads. It consists of an outer ring, an inner ring, a set of balls, and a cage that separates and maintains a consistent spacing between the balls. Here’s how ball bearings function in various applications:
- Reduction of Friction:
Ball bearings function by replacing sliding friction with rolling friction. The smooth, spherical balls minimize the contact area between the inner and outer rings, resulting in lower friction and reduced heat generation.
- Radial and Axial Load Support:
Ball bearings are designed to support both radial loads (forces perpendicular to the shaft’s axis) and axial loads (forces parallel to the shaft’s axis). The distribution of balls within the bearing ensures load-carrying capacity in multiple directions.
- Smooth Rotational Movement:
Ball bearings facilitate smooth and precise rotational movement. The rolling motion of the balls allows for controlled and continuous rotation with minimal resistance.
- Applications in Machinery:
Ball bearings are used in a wide range of machinery and equipment, including motors, generators, gearboxes, conveyors, and fans. They enable the efficient transfer of motion while reducing wear and energy losses.
- Automotive Industry:
Ball bearings are extensively used in automobiles for various applications, including wheel hubs, transmission systems, steering mechanisms, and engine components. They provide reliability and durability in challenging automotive environments.
- Industrial Machinery:
In industrial settings, ball bearings support rotating shafts and ensure the smooth operation of equipment such as pumps, compressors, and machine tools.
- High-Speed Applications:
Ball bearings are suitable for high-speed applications due to their low friction and ability to accommodate rapid rotation. They are used in applications like electric motors and aerospace components.
- Precision Instruments:
For precision instruments, such as watches, cameras, and medical devices, ball bearings provide accurate rotational movement and contribute to the overall performance of the instrument.
- Variety of Sizes and Types:
Ball bearings come in various sizes, configurations, and materials to suit different applications. Different types include deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, thrust ball bearings, and more.
In summary, ball bearings are essential components in a wide range of applications where smooth rotation, load support, and reduced friction are critical. Their versatility, reliability, and efficiency make them indispensable in industries spanning from automotive to industrial machinery to precision instruments.


editor by CX 2024-05-16
China supplier Free Samples of Original NSK. NTN. CZPT Deep Groove Ball Bearing bearing driver
Product Description
Product Description
DEEP GROOVE BALL BEARING
Deep groove ball bearing .The original list of radial ball bearings is the most widely used type of rolling bearing. It is characterized by low frictional resistance and high rotational speed. It can be used on parts that bear radial load or combined radial and axial loads at the same time, and can also be used on parts that bear axial load, such as low-power motors, Automobile and tractor gearboxes, machine tool gearboxes, general machines, tools, etc.
Deep groove ball bearing models are: deep groove ball bearing (type 60000), deep groove ball bearing with retaining groove in the outer ring (type 60000N), deep groove ball with a dust cover on 1 side and a retaining groove in the outer ring on the other side Bearing (type 60000-ZN), deep groove ball bearing with dust cover on both sides and retaining groove in outer ring (type 60000-2ZN), deep groove ball bearing with dust cover on 1 side (type 60000Z), 2 sides Deep groove ball bearing with dust cover (type 60000-2Z), deep groove ball bearing with sealing ring on 1 side (type 60000-LS, 60000-RZ), deep groove ball bearing with sealing ring on both sides (type 60000- 2LS , 60000-2RZ), flanged outer ring deep groove ball bearing (type F60000 ), flanged outer ring deep groove ball bearing with dust cover on 1 side (type F60000-Z ), There are 11 types of flanged outer ring deep groove ball bearings (type F60000-2Z ).
|
62 Series Ball Bearings : |
||||
|
NO. |
Bearing Number |
Bearing Size (dxDxB) |
Bearings Style |
Remarks |
|
1 |
6201 |
12*32*10 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
2 |
6202 |
15*35*11 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
3 |
6203 |
17*40*12 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
4 |
6204 |
20*47*14 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
5 |
6205 |
25*52*15 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
6 |
6206 |
30*62*16 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
7 |
6207 |
35*72*17 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
8 |
6208 |
40*80*18 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
9 |
6209 |
45*85*19 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
10 |
6210 |
50*90*20 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
11 |
6211 |
55*100*21 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
12 |
6212 |
60*110*22 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
13 |
6213 |
65*120*23 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
14 |
6214 |
70*125*24 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
15 |
6215 |
75*130*25 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
16 |
6216 |
80*140*26 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
17 |
6217 |
85*150*28 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
18 |
6218 |
90*160*30 |
2RS,ZZ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearing |
|
60 Series Ball Bearings : |
||||
|
NO. |
Bearing Model |
Bearings Size (dxDxB) |
Bearing Style |
Remarks |
|
1 |
6002 |
15*32*9 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
2 |
6003 |
17*35*10 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
3 |
6004 |
20*42*12 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
4 |
6005 |
25*47*12 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
5 |
6006 |
30*55*13 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
6 |
6007 |
35*62*14 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
7 |
6008 |
40*68*15 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
8 |
6009 |
45*75*16 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
9 |
6571 |
50*80*16 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
10 |
6011 |
55*90*18 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
11 |
6012 |
60*95*18 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
12 |
6013 |
65*100*18 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
13 |
6014 |
70*110*20 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
14 |
6015 |
75*115*20 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
15 |
6016 |
80*125*22 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
16 |
6017 |
85*130*22 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
17 |
6018 |
90*140*24 |
2RS ,2RZ ,ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bea |
|
63 Series Ball Bearings : |
||||
|
NO. |
Bearing Model |
Bearing Size (dxDXB) |
Bearing Style |
Remarks |
|
1 |
6301 |
12*37*12 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
2 |
6302 |
15*42*13 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
3 |
6303 |
17*47*14 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
4 |
6304 |
20*52*15 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
5 |
6305 |
25*62*17 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
6 |
6306 |
30*72*19 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
7 |
6307 |
35*80*21 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
8 |
6308 |
40*90*23 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
9 |
6309 |
45*100*25 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
10 |
6310 |
50*110*27 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
11 |
6311 |
55*120*29 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
12 |
6312 |
60*130*31 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
13 |
6313 |
65*140*33 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
14 |
6314 |
70*150*35 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
15 |
6315 |
75*160*37 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
16 |
6316 |
80*170*39 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
17 |
6317 |
85*180*41 |
2RS ,ZZ ,2Z,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
69 Series Ball Bearings : |
||||
|
NO. |
Bearing Model |
Bearing Size (dxDxB) |
Bearing Style |
Remarks |
|
1 |
6905 |
25*42*9 |
2RS, ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
2 |
6907 |
35*55*10 |
2RS, ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
3 |
6908 |
40*62*12 |
2RS, ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
|
4 |
6909 |
45*68*12 |
2RS, ZZ ,2Z ,OPEN |
Precision Bearings |
High speed and good wear resistance
Compared with similar bearings, our speed is higher and more wear-resistant
Low friction coefficient, high precision
Precision design and production, so that the product precision is higher, less friction
Low noise and longer life
Compared with similar bearings, less noise and longer life
APPLICATION
Recommended Products
Company Profile
Packaging & Shipping
FAQ
Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: We are factory. Welcome to visit our factory.
Q: How to get price ?
A: Please send inquiry directly. Our salesman replys very fast.
Q: Do you provide Free Samples ?
A: Yes, we could offer you free samples, but do not pay the cost of freight.
Q: What’s the MOQ ?
A: The MOQ depends on bearing’s model number and price.Usually the total cost will be $1000 at least.
Q: What’s your Payment Terms ?
A: T/T (Bank Wire)
Western Union
Money Grame
Paypal
Q: How long is your lead-time?
A: Generally it is 2 to 4 days if the goods are in stock, or it will be about 6 to 15 days depends on quantity. /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Package: | OEM |
|---|---|
| Delivery: | Fast |
| Structure: | Deep Groove |
| Precision Rating: | P0 P6 P5 P4 P2 |
| Number of Row: | Single Row |
| Seals Type: | Zz 2RS Open |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How does Preload Affect the Performance and Efficiency of Ball Bearings?
Preload is a crucial factor in ball bearing design that significantly impacts the performance, efficiency, and overall behavior of the bearings in various applications. Preload refers to the intentional axial force applied to the bearing’s rolling elements before it is mounted. This force eliminates internal clearance and creates contact between the rolling elements and the raceways. Here’s how preload affects ball bearing performance:
- Reduction of Internal Clearance:
Applying preload reduces the internal clearance between the rolling elements and the raceways. This eliminates play within the bearing, ensuring that the rolling elements are in constant contact with the raceways. This reduced internal clearance enhances precision and reduces vibrations during operation.
- Increased Stiffness:
Preloaded bearings are stiffer due to the elimination of internal clearance. This increased stiffness improves the bearing’s ability to handle axial and radial loads with higher accuracy and minimal deflection.
- Minimized Axial Play:
Preload minimizes or eliminates axial play within the bearing. This is especially important in applications where axial movement needs to be minimized, such as machine tool spindles and precision instruments.
- Enhanced Rigidity:
The stiffness resulting from preload enhances the bearing’s rigidity, making it less susceptible to deformation under load. This is critical for maintaining precision and accuracy in applications that require minimal deflection.
- Reduction in Ball Slippage:
Preload reduces the likelihood of ball slippage within the bearing, ensuring consistent contact between the rolling elements and the raceways. This leads to improved efficiency and better load distribution.
- Improved Running Accuracy:
Preloading enhances the running accuracy of the bearing, ensuring that it maintains precise rotational characteristics even under varying loads and speeds. This is essential for applications requiring high accuracy and repeatability.
- Optimized Performance at High Speeds:
Preload helps prevent skidding and slipping of the rolling elements during high-speed operation. This ensures that the bearing remains stable, reducing the risk of noise, vibration, and premature wear.
- Impact on Friction and Heat Generation:
While preload reduces internal clearance and friction, excessive preload can lead to higher friction and increased heat generation. A balance must be struck between optimal preload and minimizing friction-related issues.
- Application-Specific Considerations:
The appropriate amount of preload depends on the application’s requirements, such as load, speed, accuracy, and operating conditions. Over-preloading can lead to increased stress and premature bearing failure, while under-preloading may result in inadequate rigidity and reduced performance.
Overall, preload plays a critical role in optimizing the performance, accuracy, and efficiency of ball bearings. Engineers must carefully determine the right preload level for their specific applications to achieve the desired performance characteristics and avoid potential issues related to overloading or inadequate rigidity.

How do Temperature and Environmental Conditions Affect the Performance of Ball Bearings?
Temperature and environmental conditions have a significant impact on the performance and longevity of ball bearings. The operating environment can influence factors such as lubrication effectiveness, material properties, and overall bearing behavior. Here’s how temperature and environmental conditions affect ball bearing performance:
- Lubrication:
Temperature variations can affect the viscosity and flow characteristics of lubricants. Extreme temperatures can cause lubricants to become too thin or too thick, leading to inadequate lubrication and increased friction. In high-temperature environments, lubricants can degrade, reducing their effectiveness.
- Material Properties:
Temperature changes can alter the material properties of the bearing components. High temperatures can lead to thermal expansion, affecting bearing clearances and potentially causing interference between components. Extreme cold temperatures can make materials more brittle and prone to fracture.
- Clearance Changes:
Temperature fluctuations can cause changes in the internal clearance of ball bearings. For instance, at high temperatures, materials expand, leading to increased clearance. This can affect bearing performance, load distribution, and overall stability.
- Corrosion and Contamination:
Harsh environmental conditions, such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or abrasive particles, can lead to corrosion and contamination of bearing components. Corrosion weakens the material, while contamination accelerates wear and reduces bearing life.
- Thermal Stress:
Rapid temperature changes can result in thermal stress within the bearing components. Differential expansion and contraction between the inner and outer rings can lead to stress and distortion, affecting precision and bearing integrity.
- Noise and Vibration:
Temperature-related changes in material properties and internal clearances can influence noise and vibration levels. Extreme temperatures can lead to increased noise generation and vibration, affecting the overall operation of machinery.
- Lubricant Degradation:
Environmental factors like humidity, dust, and contaminants can lead to premature lubricant degradation. Oxidation, moisture absorption, and the presence of foreign particles can compromise the lubricant’s performance and contribute to increased friction and wear.
- Seal Effectiveness:
Seals and shields that protect bearings from contaminants can be affected by temperature fluctuations. Extreme temperatures can lead to seal hardening, cracking, or deformation, compromising their effectiveness in preventing contamination.
- Choosing Appropriate Bearings:
When selecting ball bearings for specific applications, engineers must consider the expected temperature and environmental conditions. High-temperature bearings, bearings with specialized coatings, and those with enhanced sealing mechanisms may be necessary to ensure reliable performance.
Overall, understanding the impact of temperature and environmental conditions on ball bearing performance is crucial for proper bearing selection, maintenance, and ensuring optimal operation in diverse industries and applications.

What is a Ball Bearing and How does it Function in Various Applications?
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to reduce friction between moving parts and support radial and axial loads. It consists of an outer ring, an inner ring, a set of balls, and a cage that separates and maintains a consistent spacing between the balls. Here’s how ball bearings function in various applications:
- Reduction of Friction:
Ball bearings function by replacing sliding friction with rolling friction. The smooth, spherical balls minimize the contact area between the inner and outer rings, resulting in lower friction and reduced heat generation.
- Radial and Axial Load Support:
Ball bearings are designed to support both radial loads (forces perpendicular to the shaft’s axis) and axial loads (forces parallel to the shaft’s axis). The distribution of balls within the bearing ensures load-carrying capacity in multiple directions.
- Smooth Rotational Movement:
Ball bearings facilitate smooth and precise rotational movement. The rolling motion of the balls allows for controlled and continuous rotation with minimal resistance.
- Applications in Machinery:
Ball bearings are used in a wide range of machinery and equipment, including motors, generators, gearboxes, conveyors, and fans. They enable the efficient transfer of motion while reducing wear and energy losses.
- Automotive Industry:
Ball bearings are extensively used in automobiles for various applications, including wheel hubs, transmission systems, steering mechanisms, and engine components. They provide reliability and durability in challenging automotive environments.
- Industrial Machinery:
In industrial settings, ball bearings support rotating shafts and ensure the smooth operation of equipment such as pumps, compressors, and machine tools.
- High-Speed Applications:
Ball bearings are suitable for high-speed applications due to their low friction and ability to accommodate rapid rotation. They are used in applications like electric motors and aerospace components.
- Precision Instruments:
For precision instruments, such as watches, cameras, and medical devices, ball bearings provide accurate rotational movement and contribute to the overall performance of the instrument.
- Variety of Sizes and Types:
Ball bearings come in various sizes, configurations, and materials to suit different applications. Different types include deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, thrust ball bearings, and more.
In summary, ball bearings are essential components in a wide range of applications where smooth rotation, load support, and reduced friction are critical. Their versatility, reliability, and efficiency make them indispensable in industries spanning from automotive to industrial machinery to precision instruments.


editor by CX 2024-05-15
China Best Sales 6702zz 2RS 15X21X4mm Bicycle Electric Motorcycle Single Row Deep Groove Ball Bearing bearing and race
Product Description
Silicon nitride rolling elements have higher hardness, making hybrid bearings suitable for difficult conditions and polluting environments;
Hybrid bearings generate low heat from friction, especially at high speeds, contributing to longer bearing life and longer lubrication intervals.
|
Model Dumber(ZZ/2RZ) |
Internal Diameter(mm) |
External Diameter(mm) |
Thickness(mm) |
|
6700 |
10 |
15 |
4 |
|
6701 |
12 |
18 |
4 |
|
6702 |
15 |
21 |
4 |
|
6703 |
17 |
23 |
4 |
|
6704 |
20 |
27 |
4 |
|
6705 |
25 |
32 |
4 |
|
6706 |
30 |
37 |
4 |
|
6707 |
35 |
44 |
5 |
|
6708 |
40 |
50 |
6 |
|
6709 |
45 |
55 |
6 |
|
6710 |
50 |
62 |
6 |
product-list-1.htmlHangZhou Terry Machinery Co.Ltd is a leading supplier of bearings, Linear motion system for CNC , Ball transfer Unit and transmission component .the growing industrial and Favorable policy of HangZhou benefit the development of Terry Machinery .Our products are utilized in industrial, motorcycle, vehicle and Automation applications. Now we are exporting to 46 countries. including USA, GBR , Germany , Spain, Poland ,Turkey ect .The Goal of Terry Machinery to provide out customers with widest range of products at competitive prices, backed with the best Service.OUR ADVANTAGE Products Our major products & Supplied:Meet all the international standards and ISO9001 -TS1694 Certificate Big volume in Stock, No MOQ required Personnel Our salespersons are well trained to accommodate your requests and speak English for your conveniences.Our technicians and engineers Experience in the Industry area exceeds 23 years Service &Quality control ,We supply detailed drawings and offer when ever necessary,We help all customers promote and improve their sales.We inspect every piece of products by ourselves before delivery.
DELIVERY & PACKING
F A QFEEDBACK
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Feature: | Long Life |
|---|---|
| Number of Row: | Single Row |
| Model Number: | 6702zz 2RS |
| Samples: |
US$ 1/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How does Preload Affect the Performance and Efficiency of Ball Bearings?
Preload is a crucial factor in ball bearing design that significantly impacts the performance, efficiency, and overall behavior of the bearings in various applications. Preload refers to the intentional axial force applied to the bearing’s rolling elements before it is mounted. This force eliminates internal clearance and creates contact between the rolling elements and the raceways. Here’s how preload affects ball bearing performance:
- Reduction of Internal Clearance:
Applying preload reduces the internal clearance between the rolling elements and the raceways. This eliminates play within the bearing, ensuring that the rolling elements are in constant contact with the raceways. This reduced internal clearance enhances precision and reduces vibrations during operation.
- Increased Stiffness:
Preloaded bearings are stiffer due to the elimination of internal clearance. This increased stiffness improves the bearing’s ability to handle axial and radial loads with higher accuracy and minimal deflection.
- Minimized Axial Play:
Preload minimizes or eliminates axial play within the bearing. This is especially important in applications where axial movement needs to be minimized, such as machine tool spindles and precision instruments.
- Enhanced Rigidity:
The stiffness resulting from preload enhances the bearing’s rigidity, making it less susceptible to deformation under load. This is critical for maintaining precision and accuracy in applications that require minimal deflection.
- Reduction in Ball Slippage:
Preload reduces the likelihood of ball slippage within the bearing, ensuring consistent contact between the rolling elements and the raceways. This leads to improved efficiency and better load distribution.
- Improved Running Accuracy:
Preloading enhances the running accuracy of the bearing, ensuring that it maintains precise rotational characteristics even under varying loads and speeds. This is essential for applications requiring high accuracy and repeatability.
- Optimized Performance at High Speeds:
Preload helps prevent skidding and slipping of the rolling elements during high-speed operation. This ensures that the bearing remains stable, reducing the risk of noise, vibration, and premature wear.
- Impact on Friction and Heat Generation:
While preload reduces internal clearance and friction, excessive preload can lead to higher friction and increased heat generation. A balance must be struck between optimal preload and minimizing friction-related issues.
- Application-Specific Considerations:
The appropriate amount of preload depends on the application’s requirements, such as load, speed, accuracy, and operating conditions. Over-preloading can lead to increased stress and premature bearing failure, while under-preloading may result in inadequate rigidity and reduced performance.
Overall, preload plays a critical role in optimizing the performance, accuracy, and efficiency of ball bearings. Engineers must carefully determine the right preload level for their specific applications to achieve the desired performance characteristics and avoid potential issues related to overloading or inadequate rigidity.

What are the Differences between Deep Groove Ball Bearings and Angular Contact Ball Bearings?
Deep groove ball bearings and angular contact ball bearings are two common types of ball bearings, each designed for specific applications and load conditions. Here are the key differences between these two types of bearings:
- Design and Geometry:
Deep Groove Ball Bearings:
Deep groove ball bearings have a simple design with a single row of balls that run along deep raceways in both the inner and outer rings. The rings are usually symmetrical and non-separable, resulting in a balanced load distribution.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings:
Angular contact ball bearings have a more complex design with two rows of balls, oriented at an angle to the bearing’s axis. This arrangement allows for the transmission of both radial and axial loads, making them suitable for combined loads and applications requiring high precision.
- Load Carrying Capacity:
Deep Groove Ball Bearings:
Deep groove ball bearings are primarily designed to carry radial loads. They can handle axial loads in both directions, but their axial load-carrying capacity is generally lower compared to angular contact ball bearings.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings:
Angular contact ball bearings are specifically designed to handle both radial and axial loads. The contact angle between the rows of balls determines the bearings’ axial load-carrying capacity. They can handle higher axial loads and are commonly used in applications with thrust loads.
- Contact Angle:
Deep Groove Ball Bearings:
Deep groove ball bearings have no defined contact angle, as the balls move in a deep groove along the raceways. They are primarily designed for radial loads.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings:
Angular contact ball bearings have a specified contact angle between the rows of balls. This contact angle allows them to carry both radial and axial loads and is crucial for their ability to handle combined loads.
- Applications:
Deep Groove Ball Bearings:
Deep groove ball bearings are commonly used in applications that primarily require radial loads, such as electric motors, pumps, and conveyor systems. They are also suitable for high-speed operation.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings:
Angular contact ball bearings are used in applications where both radial and axial loads are present, such as in machine tools, automotive wheel hubs, and aerospace components. They are especially useful for applications that require precise axial positioning and handling of thrust loads.
- Limitations:
Deep Groove Ball Bearings:
Deep groove ball bearings are not as suitable for handling significant axial loads and may experience skidding under certain conditions due to their deep raceways.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings:
Angular contact ball bearings can experience increased heat generation and wear at higher speeds due to the contact angle of the balls.
In summary, the design, load-carrying capacity, contact angle, and applications differ between deep groove ball bearings and angular contact ball bearings. Choosing the appropriate type depends on the specific load conditions and requirements of the application.

What is a Ball Bearing and How does it Function in Various Applications?
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to reduce friction between moving parts and support radial and axial loads. It consists of an outer ring, an inner ring, a set of balls, and a cage that separates and maintains a consistent spacing between the balls. Here’s how ball bearings function in various applications:
- Reduction of Friction:
Ball bearings function by replacing sliding friction with rolling friction. The smooth, spherical balls minimize the contact area between the inner and outer rings, resulting in lower friction and reduced heat generation.
- Radial and Axial Load Support:
Ball bearings are designed to support both radial loads (forces perpendicular to the shaft’s axis) and axial loads (forces parallel to the shaft’s axis). The distribution of balls within the bearing ensures load-carrying capacity in multiple directions.
- Smooth Rotational Movement:
Ball bearings facilitate smooth and precise rotational movement. The rolling motion of the balls allows for controlled and continuous rotation with minimal resistance.
- Applications in Machinery:
Ball bearings are used in a wide range of machinery and equipment, including motors, generators, gearboxes, conveyors, and fans. They enable the efficient transfer of motion while reducing wear and energy losses.
- Automotive Industry:
Ball bearings are extensively used in automobiles for various applications, including wheel hubs, transmission systems, steering mechanisms, and engine components. They provide reliability and durability in challenging automotive environments.
- Industrial Machinery:
In industrial settings, ball bearings support rotating shafts and ensure the smooth operation of equipment such as pumps, compressors, and machine tools.
- High-Speed Applications:
Ball bearings are suitable for high-speed applications due to their low friction and ability to accommodate rapid rotation. They are used in applications like electric motors and aerospace components.
- Precision Instruments:
For precision instruments, such as watches, cameras, and medical devices, ball bearings provide accurate rotational movement and contribute to the overall performance of the instrument.
- Variety of Sizes and Types:
Ball bearings come in various sizes, configurations, and materials to suit different applications. Different types include deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, thrust ball bearings, and more.
In summary, ball bearings are essential components in a wide range of applications where smooth rotation, load support, and reduced friction are critical. Their versatility, reliability, and efficiency make them indispensable in industries spanning from automotive to industrial machinery to precision instruments.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China Best Sales Linear Guide Rail Bearing 35ca1r800z0c for Goods Yard Crane deep groove ball bearing
Product Description
Roller linear CZPT rail, cylindrical linear CZPT rail, and ball linear CZPT rail are 3 types used to support and CZPT moving components to perform reciprocating linear motion in a given direction. According to the friction property, linear motion CZPT can be divided into sliding
| Brand | SHAC,H.S.A.C |
| Precision | C/H/P |
| Model | GHH/GHW/GEH/GEW/MGN/MGW |
| Size customize | Available |
| Maximum length | 4000MM |
| Raw Materail | S55C,SCM420H |
| HS CODE | 8466939000,8483300090 |
| Items packing | Plastic bag+Cartons+Plywood boxes.According to our customer’s request. |
| Payment terms | L/C,TT,Westeb Union |
| Production lead time | Base on customer required quantity,by negotiated |
| Samples | Value less than $20 free samples and sample catalogue available,sample express request pay by clients |
| Application | CNC machines,machine tools,Industrial Machinery,Pringting Machine,Paper-processing machine,automatic machines,textiles machines,electronic machinery,transport machinery,Robot,etc |
The analytical diagram of the linear CZPT rail is as follows
As follows linear guide&block are in stock:(compatible with HIWIN linear guide)
| GH series rail | GHR15,GHR20,GHR25,GHR30,GHR35,GHR45 |
| GHH..CA square block | GHH15CA,GHH20CA,GHH25CA,GHH30CA,GHH35CA,GHH45CA |
| GHW..CC flange block | GHW15CC,GHW20CC,GHW25CC,GHW30CC,GHW35CC,GHW45CC |
| GHH..HA lengthen | GHH20HA,GHH25HA,GHH30HA,GHH35HA,GHH45HA |
| GHW..HC lengthen | GHW15HC,GHW20HC,GHW25HC,GHW30HC,GHW35HC,GHW45HC |
| GE low assembly rail | GER15,GER20,GER25 |
| GEH..CA | GEH15CA,GEH20CA,GEH25CA |
| GEH..SA | GEH15SA,GEH20SA |
| GEW..CA | GEW15CA,GEW20CA,GEW25CA |
| MGN rail | MGNR5,MGR7,MGR9,MGR12,MGR15 |
| MGN..C | MGN5C,MGN7C,MGN9C,MGN12C,MGN15C |
| MGN..H | MGN7H,MGN9H,MGN12H,MGN15H |
| MGW rail | MGW7,MGW9,MGW12,MGW15 |
| MGW..C | MGW7C,MGW9C,MGW12C,MGW15C |
| MGW..H | MGW7H,MGW9H,MGW12H,MGW15H |
Performance
Support rail unit is assembled of Support Rail, LM Shaft, and Open type Linear Bushing Case.
All components are standardized for providing interchangeability and less cost and designing time.
Product Feature of Linear Support Rail Unit:
1.Interchangeable
2.Max length: 4000mm
3.High quality standard
4. Rail: Length can be cut freely.
Our Advantages
1.Our Team:
We have experienced and qualified team of marketing and sales representatives to serve our valued customers with the finest products and unsurpassed service.And have professional engineers team to assessment and development the new precision products,and make the OEM customized more easily,experienced QC team to test the products quaity ensure the goods quality before delivery out.
2.Our products:
Quality is the life .We use only the best quality material to ensure the precision of our
Product.All products we sold out are strictly selected and tested by our QC department.
3.Payment:
We accept payment via TT (Bank transfer), L/C,Western Union.
4.Shipping method:
Including DHL, UPS, TNT, FEDEX,EMS, Airfreight and by Sea,as customer required.
Precautions
Linear guides are precision components, so a considerable caution is required when using them.
Even if high-performance linear guides are used improperly, they cannot achieve the expected performance effect and are prone to damage. Therefore, when using linear guides, the following precautions should be taken:
1.Prevent rusting
When directly picking up the linear CZPT rail by hand, it is necessary to thoroughly wash the sweat off the hands and apply high-quality mineral oil before proceeding with the operation. Special attention should be paid to rust prevention during the rainy season and summer.
2.Keep the environment clean
Keeping the linear CZPT rail and its surrounding environment clean, even small dust that cannot be seen by the naked eye entering the CZPT rail, will increase the wear, vibration, and noise of the CZPT rail.
3.Installation should be careful and careful
When using and installing linear CZPT rails, it is necessary to be careful and careful. It is not allowed to forcefully punch, directly hit the CZPT rails with a hammer, or transmit pressure through rolling elements.
4.Installation tools should be suitable
Use suitable and accurate installation tools for the linear CZPT rail, and try to use specialized tools as much as possible, avoiding the use of fabrics and short fibers.
Application:
1. Automatic controlling machine
2. Semi-conductor industry
3. General industry machinery
4. Medical equipment
5. Solar energy equipment
6. Machine tool
7. Parking system
8. High-speed rail and aviation transportation equipment, etc.
Packaging & Shipping
Package of Linear Slide Unit:
1. Standard export packing
2. According to the customers’ request
Shipping:
1. Lead time: around 8-15 days, pls confirm before order;
2. Incoterm: FOB, C&F, CIF;
3. Delivery Cost: Pls advise the port of destination and we could assist to check it for you;
4. Payment Term: T/T; L/C; PayPal; Alibaba Trade Assurance.
FAQ
1.Is the company a production factory or a trading company?
ZheJiang Dente International Trade Co.,Ltd is a manufacturing enterprise focusing on bearings and integrating research, production and sales.
2.How many the MOQ of your company?
Depending on the size of the bearing, the MOQ is variable, if you are interested, you can contact me for a quote.
3.Does the company accept OEM or customized bearings?
In addition to standard products, we also supply non-standard and modified standard products for special application. Meanwhile, we provide OEM service.
4.What are the company’s delivery terms?
We can accept EXW,FOB,CFR,CIF,etc. You can choose the 1 which is the most convenient cost effective for you.
5.What is your delivery time?
Most orders will be shipped within 7-15 days of payment being received.
Any problems, pls feel free to contact us.100% after-sales service!
We can supply high-quality bearing products with competitive price and the shortest delivery time if you choose us!
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Warehouse Crane, Shipboard Crane, Goods Yard Crane, Building Crane, Workshop Crane |
|---|---|
| Material: | Steel |
| Structure: | Tyre Crane |
| Samples: |
US$ 0.3/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample Chrome steel
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
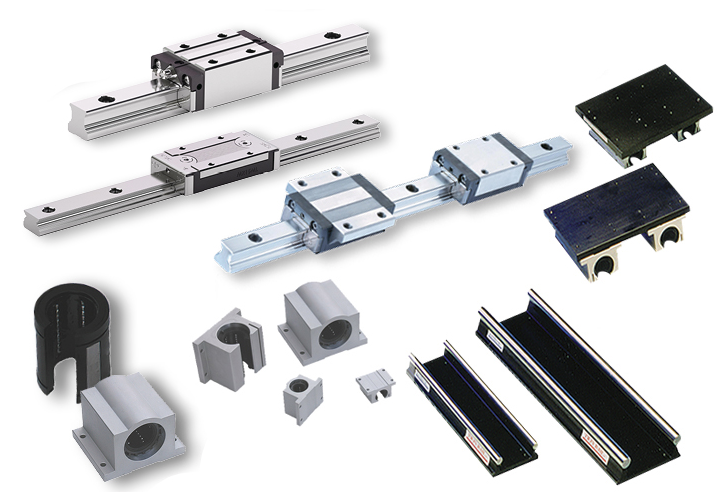
Challenges and Solutions for Addressing Friction and Wear in Linear Bearings
Friction and wear are common challenges in linear bearings that can impact their performance and lifespan. Here are the challenges and some solutions to address them:
- 1. Challenge: Friction:
Friction between the bearing components can lead to increased energy consumption, heat generation, and reduced efficiency.
- Solution: Lubrication:
Proper lubrication is essential to minimize friction. Lubricants reduce the contact between moving parts, allowing smoother motion and reducing wear. Choosing the right lubricant and applying it correctly can significantly mitigate friction-related issues.
- 2. Challenge: Wear:
Continuous movement can lead to wear on the bearing surfaces, affecting precision and performance over time.
- Solution: Regular Maintenance:
Implementing a regular maintenance schedule can help monitor wear and replace worn components before they compromise performance. This includes cleaning, re-lubrication, and periodic inspection of the bearing’s condition.
- 3. Challenge: Contaminants:
Dust, debris, and foreign particles can enter the bearing system, leading to increased friction and accelerated wear.
- Solution: Sealing and Protection:
Using seals, covers, or protective enclosures can help prevent contaminants from entering the bearing system. These protective measures maintain the integrity of the lubricant and extend the bearing’s lifespan.
- 4. Challenge: Improper Installation:
If linear bearings are not installed correctly, misalignment and uneven load distribution can contribute to friction and wear.
- Solution: Precise Installation:
Follow manufacturer guidelines for proper installation, ensuring accurate alignment and even load distribution. This reduces the risk of premature wear and ensures optimal performance.
- 5. Challenge: Inadequate Lubrication:
If the linear bearings are under-lubricated or over-lubricated, it can lead to increased friction and wear.
- Solution: Lubrication Management:
Monitor and manage lubrication levels to ensure they are within the recommended range. Regularly assess the lubricant’s condition and replenish as needed to maintain optimal performance.
- 6. Challenge: High Loads and Speeds:
High loads and speeds can increase friction and wear on linear bearings.
- Solution: Proper Selection:
Select linear bearings that are designed to handle the specific loads and speeds of the application. This ensures that the bearings can operate effectively under the given conditions.
Addressing friction and wear challenges in linear bearings requires a combination of proper maintenance practices, appropriate lubrication, protective measures, and careful selection of bearings. By implementing these solutions, the performance and longevity of linear bearings can be optimized.

Role of Linear Bearings in Heavy Load and High Precision Applications
Linear bearings are essential components in applications that require the combined capabilities of handling heavy loads and maintaining high precision. They serve a critical role in such scenarios:
- Heavy Load Handling:
Linear bearings are designed to support and guide heavy loads along a linear path. They distribute the weight evenly, reducing friction and wear on the moving components and ensuring smooth and stable movement.
- Precision Motion Control:
Linear bearings enable precise and accurate control over the motion of heavy loads. This precision is crucial in applications where components need to be positioned or moved with extremely fine tolerances.
- Reduced Friction:
Linear bearings are engineered to minimize friction between moving parts, even under heavy load conditions. This not only improves efficiency but also enhances the accuracy of movement.
- Smooth Movement:
Linear bearings provide smooth and consistent movement, ensuring that heavy loads can be guided and positioned without jarring or sudden stops. This is particularly important for applications requiring controlled and gentle motion.
- Reduced Wear and Maintenance:
By reducing friction and wear, linear bearings extend the operational lifespan of heavy-load equipment. This translates to lower maintenance requirements and longer intervals between servicing.
- Optimized Performance:
Linear bearings contribute to the overall performance of heavy-load systems by allowing them to operate smoothly, accurately, and reliably. This is critical in applications where precision and consistency are paramount.
- Wide Range of Industries:
Linear bearings find application in various industries, including manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery, where heavy loads need to be moved with high precision.
Overall, linear bearings serve as a cornerstone in applications that demand the simultaneous management of heavy loads and precise movement. They ensure that heavy machinery and equipment can function efficiently and accurately while maintaining the safety and integrity of the entire system.
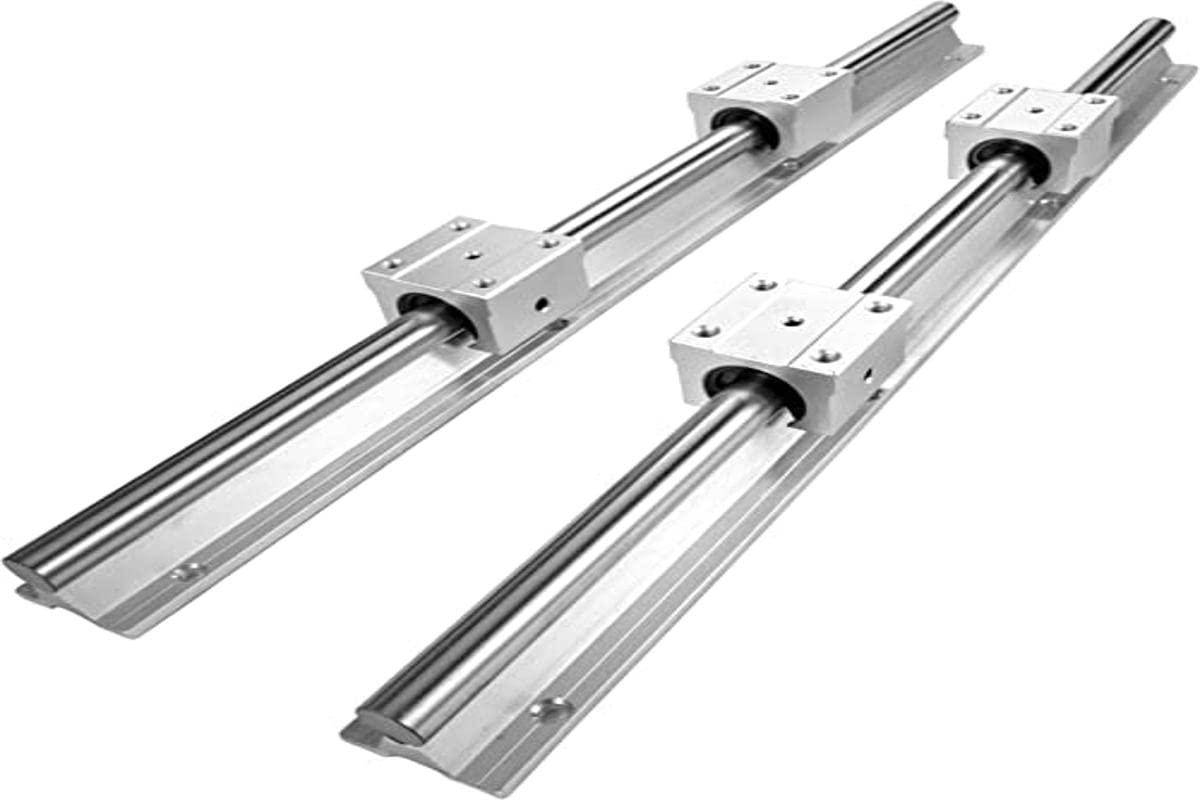

Advantages of Linear Bearings over Other Bearing Types
Linear bearings offer several distinct advantages when compared to other types of bearings, particularly in applications that require controlled linear motion. These benefits contribute to their widespread use across various industries:
- Precise Linear Motion:
Linear bearings are designed specifically for linear motion, providing accurate and controlled movement along a defined path. This precision is essential in applications that demand accurate positioning and repeatability.
- Low Friction:
Linear bearings are designed to minimize friction during motion. The reduced friction translates to smoother movement, reduced wear, and improved efficiency, making them suitable for applications requiring consistent motion.
- High Load Capacity:
Linear bearings can handle significant loads in both radial and axial directions. This capability allows them to support heavy components and maintain stability under various loads.
- Minimal Maintenance:
Due to their design and minimal contact between moving parts, linear bearings require less maintenance compared to other types of bearings. This is particularly advantageous in hard-to-reach or inaccessible areas.
- Guided Motion:
Linear bearings provide guided and constrained motion along a single axis. This guidance eliminates the need for complex guiding mechanisms, reducing design complexity and simplifying assembly.
- Compact Design:
Linear bearings have a compact form factor, making them suitable for applications with limited space. Their small footprint allows for efficient use of available area.
- Low Noise and Vibration:
Linear bearings generate minimal noise and vibration during operation, contributing to quieter and more comfortable working environments in applications such as medical devices and precision machinery.
- Smooth Movement:
Linear bearings offer smooth and consistent movement, essential for applications requiring continuous and controlled motion, such as robotic systems and conveyor belts.
- Customization:
Linear bearings can be designed to fit specific application requirements, including load capacity, travel distance, and environmental conditions. This customization enhances their suitability for diverse applications.
- Reduced Wear:
The low friction and guided motion of linear bearings result in reduced wear on both the bearing and the mating surface, leading to longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Overall, the benefits of using linear bearings make them a preferred choice in applications that demand accurate linear motion, efficient load handling, and reduced maintenance. Their ability to deliver precision, stability, and reliability contributes to improved performance across various industries.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China factory CZPT Deep Groove Ball Bearing List 6102 6202 6302 6402 bearing and race
Product Description
koyo deep groove ball bearing list
We can supply Bearings And Ball Bearings, please feel free to contact us!
Product Parameters
| Product Name | Bearing |
| Brand | KOYO |
| Model | |
| Warranty | 1 Year |
| Application | Industrial Ect |
| Technical consulting support | Yes |
Real Picture
Company Profile
ZheJiang CZPT Xing Trading Co.,Ltd is a professional supplier of Inverter,Servo Motor,PLC And HMI with 20 years production experience.
Our main products Inverter,Servo Motor,PLC And HMI are widely applied to the field of industrial automation control.
We guaranteed 100% new brand original, and we have a lot of stock with fast delivery. The technical support and after sale service
is provided and customer’s questions will be responded in the first time.
Main Products:
1. Servo system products
2. Linear motion products
3. Sensor products
4. Frequency converter, PLC,
FAQ
1.Q: How about the warranty ?
A: Aiwell provide 12 months warranty for all the goods from us , and you can refund the goods with any quality problem in 15 days.
2.Q: Other supplier have a better pice than yours.
A: “To create more benefit fir clients”is our belief, if you have a better price , please let Aiwell know , we will try best to meet your price and support you.
3.Q: We have not cooperated before , how can we believe you ?
A: For our first order , you can pay after we prepare the goods.
4.Q: What about shipment ?
A: We have DHL forwarder with competitive price , of course , cutsomers can also use their own freight forwarders.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Contact Angle: | 60° |
|---|---|
| Aligning: | Non-Aligning Bearing |
| Separated: | Separated |
| Rows Number: | Double |
| Load Direction: | Radial Bearing |
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the Challenges Associated with Noise Reduction in Ball Bearings?
Noise reduction in ball bearings is a crucial consideration, especially in applications where noise levels must be minimized for operational efficiency and user comfort. While ball bearings are designed to operate smoothly, there are several challenges associated with reducing noise in their operation:
- Vibration:
Vibration generated by the movement of rolling elements and raceways can lead to noise. Even minor irregularities in bearing components or the mounting system can cause vibration that translates into audible noise.
- Bearing Type and Design:
The type and design of the ball bearing can impact noise generation. For example, deep groove ball bearings are known for their quiet operation, while angular contact bearings can generate more noise due to their higher contact angles.
- Lubrication:
Improper or inadequate lubrication can result in increased friction and wear, leading to noise. Choosing the right lubricant and maintaining proper lubrication levels are essential for reducing noise in ball bearings.
- Bearing Clearance and Preload:
Incorrect clearance or preload settings can lead to noise issues. Excessive clearance or inadequate preload can cause the rolling elements to impact the raceways, resulting in noise during rotation.
- Material and Manufacturing Quality:
The quality of materials and manufacturing processes can affect noise levels. Inconsistent or low-quality materials, improper heat treatment, or manufacturing defects can lead to noise generation during operation.
- Surface Finish:
The surface finish of the rolling elements and raceways can impact noise. Rough surfaces can generate more noise due to increased friction and potential irregularities.
- Sealing and Shielding:
Seals and shields that protect bearings can influence noise levels. While they are necessary for contamination prevention, they can also cause additional friction and generate noise.
- Operating Conditions:
External factors such as temperature, speed, and load can influence noise levels. High speeds or heavy loads can amplify noise due to increased stress on the bearing components.
- Wear and Deterioration:
As ball bearings wear over time, noise levels can increase. Worn components or inadequate lubrication can lead to more significant noise issues as the bearing operates.
To address these challenges and reduce noise in ball bearings, manufacturers and engineers employ various techniques, such as optimizing design, selecting suitable bearing types, using proper lubrication, maintaining accurate preload settings, and ensuring high-quality materials and manufacturing processes. Noise reduction efforts are essential to improve overall product quality, meet noise regulations, and enhance user experience in various applications.

Are there any Industry Standards or Certifications that Ball Bearings should Meet?
Yes, there are several industry standards and certifications that ball bearings should meet to ensure their quality, performance, and reliability. These standards help manufacturers, engineers, and customers assess the suitability of bearings for specific applications. Some of the key standards and certifications for ball bearings include:
- ISO Standards:
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed a series of standards related to ball bearings. ISO 15 defines dimensions, boundary dimensions, and tolerances for radial bearings. ISO 281 specifies dynamic load ratings and calculation methods for bearings’ life calculations.
- ABEC (Annular Bearing Engineering Committee) Ratings:
ABEC ratings are commonly used in North America to indicate the precision and performance of ball bearings. Ratings range from ABEC 1 (lowest precision) to ABEC 9 (highest precision). However, it’s important to note that ABEC ratings focus primarily on dimensional tolerances and do not encompass all aspects of bearing quality.
- DIN Standards:
The German Institute for Standardization (Deutsches Institut für Normung, DIN) has published various standards related to ball bearings. DIN 625 covers dimensions for deep groove ball bearings, while DIN 616 provides guidelines for precision angular contact ball bearings.
- JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards):
JIS standards are used in Japan and internationally to define the characteristics and dimensions of various products, including ball bearings. JIS B 1512 outlines the classification and dimensions of rolling bearings.
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) Standards:
ASTM has standards that cover various aspects of bearing testing, performance, and materials. ASTM F2215, for instance, specifies the requirements for ball bearings used in surgical implants.
- CE Marking:
CE marking indicates that a product complies with European Union health, safety, and environmental requirements. It may be required for bearings used in machinery intended to be sold within the EU market.
- Industry-Specific Standards:
Various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and nuclear, have specific standards or certifications that bearings must meet to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with industry-specific requirements.
- Quality Management Systems:
Manufacturers that adhere to quality management systems, such as ISO 9001, demonstrate their commitment to consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. Certification to these systems indicates that the manufacturing process follows established protocols and best practices.
When selecting ball bearings, it’s important to consider the relevant standards and certifications that align with the application’s requirements. This ensures that the bearings meet recognized quality and performance criteria, ultimately contributing to reliable and efficient operation.

How does Lubrication Impact the Performance and Lifespan of Ball Bearings?
Lubrication plays a critical role in the performance and lifespan of ball bearings. Proper lubrication ensures smooth operation, reduces friction, minimizes wear, and prevents premature failure. Here’s how lubrication impacts ball bearings:
- Friction Reduction:
Lubrication creates a thin film between the rolling elements (balls) and the raceways of the bearing. This film reduces friction by separating the surfaces and preventing direct metal-to-metal contact. Reduced friction results in lower energy consumption, heat generation, and wear.
- Wear Prevention:
Lubricants create a protective barrier that prevents wear and damage to the bearing’s components. Without proper lubrication, the repeated rolling and sliding of the balls against the raceways would lead to accelerated wear, surface pitting, and eventual failure.
- Heat Dissipation:
Lubricants help dissipate heat generated during operation. The rolling elements and raceways can generate heat due to friction. Adequate lubrication carries away this heat, preventing overheating and maintaining stable operating temperatures.
- Corrosion Resistance:
Lubrication prevents moisture and contaminants from coming into direct contact with the bearing’s surfaces. This helps protect the bearing against corrosion, rust, and the formation of debris that can compromise its performance and longevity.
- Noise Reduction:
Lubricated ball bearings operate quietly because the lubricant cushions and dampens vibrations caused by the rolling motion. This noise reduction is crucial in applications where noise levels need to be minimized.
- Seal Protection:
Lubricants help maintain the effectiveness of seals or shields that protect the bearing from contaminants. They create a barrier that prevents particles from entering the bearing and causing damage.
- Improved Efficiency:
Properly lubricated ball bearings operate with reduced friction, leading to improved overall efficiency. This is especially important in applications where energy efficiency is a priority.
- Lifespan Extension:
Effective lubrication significantly extends the lifespan of ball bearings. Bearings that are properly lubricated experience less wear, reduced fatigue, and a lower likelihood of premature failure.
- Selection of Lubricant:
Choosing the right lubricant is essential. Factors such as speed, temperature, load, and environmental conditions influence the choice of lubricant type and viscosity. Some common lubricant options include grease and oil-based lubricants.
- Regular Maintenance:
Regular lubrication maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal bearing performance. Bearings should be inspected and relubricated according to manufacturer recommendations and based on the application’s operating conditions.
In summary, proper lubrication is essential for the optimal performance, longevity, and reliability of ball bearings. It reduces friction, prevents wear, dissipates heat, protects against corrosion, and contributes to smooth and efficient operation in various industrial and mechanical applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China Standard Motorcycle Parts Bearing 6000/6001/6002/6003 Deep Groove Ball Bearing bearing assembly
Product Description
Product Description
BEARING INNER RING
A steel ball with a common steel ball or roller rolling on the outer surface of the inner ring.
RUBBER SEALAFTER CODE: RS 2RS Z ZZ
The sealing material is made of skeleton rubber and has good dust-proof effect, which can prevent any foreign matter from invading and dust and water in a harsh environment.
Main Features1.Bearing moves very Fast & Quiet, with very smooth hand feeling
2.High precision, long life, low noise
3.High-end technology
4.Good after-sales service
Company Profile
HangZhou CZPT Machinery Technology Co., Ltd is industry and trade company which modern enterprise integrating scientific research, development, manufacture and trading. Based on integrity, responsibility and cooperation, our company have professional R&D and sales team, providing one-stop service for customers. Our company mainly products is Bearing, Jack Hammer, Screw Air Compressor, Piston Air Compressor and Other Machinery Hardware Product etc.
After many years of production and research and development, we have obtained more than 20 national patents. The products are sold at home and abroad and are well received by customers. Our products sold at home and abroad, after get the self-managemert import and export rights, our products are exported to Vietnam, Indonesia, Philippines, Cambodia, Pakistan, Afghanistan and other countries and regions.
Application
Electric motors and generators
Agriculture
Material handling
Industrial transmissions
Food and beverage
Industrial pumps
Industrial fans
Two and 3 wheelers
Cars and light trucks
Packaging & Shipping
Customer feedback
FAQ
Q1: Are you factory or trade company?
A1: We are factory. And we have our own trading company.
Q2: What the exactly address of your factory?
A2: Our company is located in Xihu (West Lake) Dis. East Road, Xihu (West Lake) Dis. District, HangZhou, ZHangZhoug, China.
Q3: Will you provide some spare parts of the machines?
A3: Yes, of course.
Q4: What about the voltage of products? Can they be customized?
A4: Yes, of course. The voltage can be customized according to your equipment.
Q5: Which payment term can you accept?
A5: 30% T/T in advance, 70% T/T against the B/L copy.
Q6: Can you accept OEM orders?
A6: Yes, with professional design team, OEM orders are highly welcome.
Q7: Which trade term can you accept?
A7: Available trade terms: FOB, CIF, CFR, EXW, CPT, etc.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Provided |
|---|---|
| Type: | Engine Bearing |
| Material: | Chrome Steel |
| Tolerance: | P0 |
| Clearance: | C2 |
| ABS: | Without ABS |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the Materials Typically Used in Manufacturing Ball Bearings and Their Advantages?
Ball bearings are manufactured using a variety of materials, each chosen for its specific properties and advantages in various applications. Here are some commonly used materials in ball bearing manufacturing and their respective benefits:
- High-Carbon Chrome Steel (AISI 52100):
This is the most common material used for ball bearing manufacturing. It offers excellent hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength. High-carbon chrome steel bearings are suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial machinery to automotive components.
- Stainless Steel (AISI 440C, AISI 304, AISI 316):
Stainless steel bearings are corrosion-resistant and suitable for applications where moisture, chemicals, or exposure to harsh environments are concerns. AISI 440C offers high hardness and corrosion resistance, while AISI 304 and AISI 316 provide good corrosion resistance and are often used in food and medical industries.
- Ceramic:
Ceramic bearings use silicon nitride (Si3N4) or zirconia (ZrO2) balls. Ceramic materials offer high stiffness, low density, and excellent resistance to corrosion and heat. Ceramic bearings are commonly used in high-speed and high-temperature applications, such as in aerospace and racing industries.
- Plastic (Polyamide, PEEK):
Plastic bearings are lightweight and offer good corrosion resistance. Polyamide bearings are commonly used due to their low friction and wear properties. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) bearings provide high-temperature resistance and are suitable for demanding environments.
- Bronze:
Bronze bearings are often used in applications where self-lubrication is required. Bronze has good thermal conductivity and wear resistance. Bearings made from bronze are commonly used in machinery requiring frequent starts and stops.
- Hybrid Bearings:
Hybrid bearings combine steel rings with ceramic balls. These bearings offer a balance between the advantages of both materials, such as improved stiffness and reduced weight. Hybrid bearings are used in applications where high speeds and low friction are essential.
- Specialty Alloys:
For specific applications, specialty alloys may be used to meet unique requirements. For example, bearings used in extreme temperatures or corrosive environments may be made from materials like titanium or hastelloy.
- Coated Bearings:
Bearings may also be coated with thin layers of materials like diamond-like carbon (DLC) or other coatings to enhance performance, reduce friction, and improve wear resistance.
The choice of material depends on factors such as application requirements, operating conditions, load, speed, and environmental factors. Selecting the right material is essential for ensuring optimal bearing performance, longevity, and reliability in diverse industries and applications.

What Role do Seals and Shields Play in Protecting Ball Bearings from Dirt and Debris?
Seals and shields are critical components of ball bearings that play a crucial role in protecting them from dirt, debris, moisture, and contaminants in various applications. These protective features help maintain the integrity of the bearing’s internal components and ensure reliable operation. Here’s how seals and shields contribute to bearing protection:
- Contaminant Exclusion:
Seals and shields create a physical barrier between the external environment and the bearing’s interior. They prevent dust, dirt, water, and other contaminants from entering the bearing and coming into contact with the rolling elements and raceways.
- Lubrication Retention:
Seals and shields help retain lubrication within the bearing. They prevent the lubricant from escaping and contaminants from entering, ensuring that the bearing remains properly lubricated for smooth operation and reduced friction.
- Corrosion Prevention:
Seals and shields protect bearing components from exposure to moisture and corrosive substances. By preventing moisture ingress, they help extend the bearing’s lifespan by minimizing the risk of corrosion-related damage.
- Extended Bearing Life:
Seals and shields contribute to the overall longevity of the bearing by reducing wear and damage caused by contaminants. They help maintain a clean internal environment, which promotes proper rolling contact and minimizes the risk of premature failure.
- Enhanced Performance in Harsh Environments:
In applications exposed to harsh conditions, such as outdoor machinery or industrial settings, seals and shields are vital. They protect bearings from abrasive particles, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, ensuring reliable performance despite challenging conditions.
- Noise and Vibration Reduction:
Seals and shields can help reduce noise and vibration generated by the bearing. They provide additional damping and stability, contributing to smoother operation and enhanced user comfort in noise-sensitive applications.
- Customized Protection:
Manufacturers offer a variety of seal and shield designs to suit different application requirements. Some seals provide higher levels of protection against contamination, while others are designed for high-speed or high-temperature environments.
- Trade-Offs:
While seals and shields offer significant benefits, they can also introduce some friction due to contact with the bearing’s inner or outer ring. Engineers must balance the level of protection with the desired operating characteristics, considering factors like friction, speed, and environmental conditions.
Overall, seals and shields play a vital role in maintaining the integrity and performance of ball bearings. By effectively preventing contaminants from entering and preserving lubrication, they ensure the smooth and reliable operation of machinery and equipment in a wide range of applications.

What Factors should be Considered when Selecting a Ball Bearing for a Particular Application?
Selecting the right ball bearing for a specific application involves careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability. Here are the key factors that should be taken into account:
- Load Type and Magnitude:
Determine the type of load (radial, axial, or combined) and the magnitude of the load that the bearing will need to support. Choose a bearing with the appropriate load-carrying capacity to ensure reliable operation.
- Speed and Operating Conditions:
Consider the rotational speed of the application and the operating conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants. Different bearing types and materials are suited for varying speeds and environments.
- Accuracy and Precision:
For applications requiring high accuracy and precision, such as machine tool spindles or optical instruments, choose high-precision bearings that can maintain tight tolerances and minimize runout.
- Space Limitations:
If the application has limited space, choose miniature or compact ball bearings that can fit within the available dimensions without compromising performance.
- Thrust and Radial Loads:
Determine whether the application requires predominantly thrust or radial load support. Choose the appropriate type of ball bearing (thrust, radial, or angular contact) based on the primary load direction.
- Alignment and Misalignment:
If the application experiences misalignment between the shaft and housing, consider self-aligning ball bearings that can accommodate angular misalignment.
- Mounting and Installation:
Consider the ease of mounting and dismounting the bearing. Some applications may benefit from features like flanges or snap rings for secure installation.
- Lubrication and Maintenance:
Choose a bearing with appropriate lubrication options based on the application’s speed and temperature range. Consider whether seals or shields are necessary to protect the bearing from contaminants.
- Environmental Conditions:
Factor in the operating environment, including exposure to corrosive substances, chemicals, water, or dust. Choose materials and coatings that can withstand the specific environmental challenges.
- Bearing Material:
Select a bearing material that suits the application’s requirements. Common materials include stainless steel for corrosion resistance and high-carbon chrome steel for general applications.
- Bearing Arrangement:
Consider whether a single-row, double-row, or multiple bearings in a specific arrangement are needed to accommodate the loads and moments present in the application.
By carefully evaluating these factors, engineers and designers can choose the most suitable ball bearing that aligns with the specific demands of the application, ensuring optimal performance, durability, and overall operational efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China manufacturer Miniature Bearing 608zz 608 2RS Deep Groove Ball Bearing with Bearing Size 8X22X7mm bearing bronze
Product Description
Product Description
Deep Groove Ball bearing 608
Main Dimensions & Performance Data
| d |
25 mm |
Bore diameter |
| D |
37 mm |
Outside diameter |
| B |
7 mm |
Width |
| Cr |
10.600 N |
Basic dynamic load rating, radial |
| C0r |
5.000 N |
Basic static load rating, radial |
| Cur |
340 N |
Fatigue load limit, radial |
| nG |
15.300 1/min |
Limiting speed |
| ≈m |
0,571 kg |
Weight |
Mounting dimensions
| da min |
23,2 mm |
Minimum diameter shaft shoulder |
| Da max |
38,8 mm |
Maximum diameter of housing shoulder |
| ra max |
0,6 mm |
Maximum fillet radius |
Dimensions
| rmin |
0,6 mm |
Minimum chamfer dimension |
| D1 |
35,45 mm |
Shoulder diameter outer ring |
| D2 |
37,38 mm |
Caliber diameter outer ring |
| d1 |
26,55 mm |
Shoulder diameter inner ring |
| d2 |
25,38 mm |
Caliber diameter inner ring |
Temperature range
| Tmin |
-20 °C |
Operating temperature min. |
| Tmax |
100 °C |
Operating temperature max. |
Calculation factors
| f0 |
13,8 |
Calculation factor |
Key Features
2RS bearing and ZZ bearing are Precision Metric Ball Bearing manufactured with both sides rubber sealed and shield and is pre-lubricated with Grease allowing it to be ready for use upon delivery. It is a Chrome Steel Metric Ball Bearing that can withstand both moderate radial and axial loads while providing high performance. Our 6000 Series Extra Light Duty Ball Bearings are available either Open, Metal Shielded, or with Rubber Sealed Closures and are pre-lubricated with grease or light oil.
Applications / Industries
Metric Ball Bearings are used in a range of applications and are ideal for limited space applications including Robotics, Vacuum Cleaners, Small Spindles, Dental Drills, Surgical Saws, Cordless Drills, Band Saws, Impact Wrenches, among others.
REBBER COVER SEAL
It can prevent the intrusion of any foreign matter and has a strong dust-proof effect. It is recommended for use in harsh environments.
IRON COVER SEAL
Compared with rubber seals, the speed is higher and the dust-proof effect is good. It is recommended when there is dust and no liquid impurities.
OPEN WITHOUT SEAL
The rotation speed is higher than the other 2 types, and the rolling resistance is low.
Deep groove ball bearing
Single row deep groove ball bearings are particularly versatile, have low friction and are optimized for low noise and low vibration, which enables high rotational speeds. They accommodate radial and axial loads in both directions, are easy to mount, and require less maintenance than many other bearing types.
- Simple, versatile and robust design
- Low friction
- High-speed capability
- Accommodate radial and axial loads in both directions
- Require little maintenance
More series of deep groove ball bearing
Tip: Here are only part of the model numbers. Please contact us for full catalog.
| Deep Groove Ball Bearing Catalog | ||||||||
| Number | Specification | Rated Load(KN) | Speed(r/min) | Weight | ||||
| D(mm) | D(mm) | W(mm) | Cr(N) | Cor(N) | Grease | Oil | kg | |
| 6000 | 10 | 26 | 8 | 4.55 | 1.96 | 20000 | 28000 | 0.019 |
| 6001 | 12 | 28 | 8 | 5.1 | 2.39 | 19000 | 26000 | 0.571 |
| 6002 | 15 | 32 | 9 | 5.6 | 2.84 | 18000 | 24000 | 0.03 |
| 6003 | 17 | 35 | 10 | 6.8 | 3.35 | 17000 | 22000 | 0.039 |
| 6004 | 20 | 42 | 12 | 9.4 | 5.05 | 15000 | 19000 | 0.069 |
| 6005 | 25 | 47 | 12 | 10.1 | 5.85 | 13000 | 17000 | 0.08 |
| 6006 | 30 | 55 | 13 | 13.2 | 8.3 | 12000 | 15000 | 0.116 |
| 6007 | 35 | 62 | 14 | 16 | 10.3 | 10000 | 13000 | 0.155 |
| 6008 | 40 | 68 | 15 | 16.8 | 11.5 | 8000 | 11000 | 0.185 |
| 6009 | 45 | 75 | 16 | 21 | 15.1 | 7200 | 9000 | 0.231 |
| 6571 | 50 | 80 | 16 | 21.8 | 16.6 | 6400 | 7800 | 0.25 |
| 6011 | 55 | 90 | 18 | 28.3 | 21.2 | 5700 | 7000 | 0.362 |
| 6012 | 60 | 95 | 18 | 29.5 | 23.2 | 5300 | 6300 | 0.385 |
| 6013 | 65 | 100 | 18 | 30.5 | 25.2 | 5040 | 6000 | 0.421 |
| 6014 | 70 | 110 | 20 | 38 | 31 | 4800 | 5600 | 0.604 |
| 6015 | 75 | 115 | 20 | 39.5 | 33.5 | 4480 | 5360 | 0.604 |
| 6016 | 80 | 125 | 22 | 47.5 | 40 | 4240 | 5040 | 0.854 |
| 6017 | 85 | 130 | 22 | 49.5 | 43 | 4000 | 4800 | 0.89 |
| 6018 | 90 | 140 | 24 | 58 | 49.5 | 3840 | 4480 | 1.02 |
| 6019 | 95 | 145 | 24 | 60.5 | 54 | 3600 | 4240 | 1.08 |
| 6571 | 100 | 150 | 24 | 60 | 54 | 3440 | 4000 | 1.15 |
| 6571 | 105 | 160 | 26 | 72.5 | 65.5 | 3200 | 3840 | 1.59 |
| 6571 | 110 | 170 | 28 | 82 | 73 | 3040 | 3600 | 1.96 |
| 6571 | 120 | 180 | 28 | 85 | 79.5 | 2720 | 3200 | 2.07 |
| 6026 | 130 | 200 | 33 | 106 | 101 | 2560 | 3040 | 3.16 |
| 6571 | 140 | 210 | 33 | 110 | 109 | 2400 | 2880 | 3.35 |
| 6030 | 150 | 225 | 35 | 126 | 126 | 2080 | 2560 | 4.08 |
| 6032 | 160 | 240 | 38 | 143 | 144 | 1920 | 2400 | 5.05 |
| 6200 | 10 | 30 | 9 | 4.056 | 1.888 | 19200 | 24000 | 0.032 |
| 6201 | 12 | 32 | 10 | 5.512 | 2.48 | 17600 | 22400 | 0.037 |
| 6202 | 15 | 35 | 11 | 6.24 | 3 | 15200 | 19200 | 0.045 |
| 6203 | 17 | 40 | 12 | 7.648 | 3.8 | 13600 | 16000 | 0.065 |
| 6204 | 20 | 47 | 14 | 10.16 | 5.24 | 12000 | 14400 | 0.11 |
| 6205 | 25 | 52 | 15 | 11.2 | 6.24 | 9600 | 12000 | 0.13 |
| 6206 | 30 | 62 | 16 | 15.6 | 8.96 | 8000 | 10400 | 0.2 |
| 6207 | 35 | 72 | 17 | 20.4 | 12.24 | 7200 | 8800 | 0.29 |
| 6208 | 40 | 8 | 18 | 24.56 | 15.2 | 6800 | 8000 | 0.37 |
| 6209 | 45 | 85 | 19 | 26.56 | 17.28 | 6000 | 7200 | 0.41 |
| 6210 | 50 | 90 | 20 | 28.08 | 18.56 | 5600 | 6800 | 0.46 |
| 6211 | 55 | 100 | 21 | 34.88 | 23.2 | 5040 | 6000 | 0.61 |
| 6212 | 60 | 110 | 22 | 38 | 26 | 4800 | 5600 | 0.78 |
| 6213 | 65 | 120 | 23 | 44.72 | 32.4 | 4240 | 5040 | 0.99 |
| 6214 | 70 | 125 | 24 | 48.4 | 36 | 4000 | 4800 | 1.05 |
| 6215 | 75 | 130 | 25 | 53.04 | 39.2 | 4480 | 5360 | 1.2 |
| 6216 | 80 | 140 | 26 | 56.16 | 44 | 3600 | 4240 | 1.4 |
| 6217 | 85 | 150 | 28 | 66.56 | 51.2 | 3440 | 4000 | 1.8 |
| 6218 | 90 | 160 | 30 | 76.48 | 58.8 | 3040 | 3600 | 2.15 |
| 6219 | 95 | 170 | 32 | 86.4 | 65.2 | 2880 | 3440 | 2.6 |
| 6220 | 100 | 180 | 34 | 99.2 | 74.4 | 2720 | 3200 | 3.15 |
| 6221 | 105 | 190 | 36 | 106.4 | 83.2 | 2560 | 3040 | 3.7 |
| 6222 | 110 | 200 | 38 | 114.4 | 94.4 | 2400 | 2880 | 4.35 |
| 6224 | 120 | 215 | 40 | 116.8 | 94.4 | 2240 | 2720 | 5.15 |
| 6226 | 130 | 230 | 40 | 124.8 | 105.6 | 2080 | 2560 | 5.8 |
| 6228 | 140 | 250 | 42 | 132 | 120 | 1920 | 2400 | 7.45 |
| 6230 | 150 | 270 | 45 | 139.2 | 132.8 | 1600 | 2080 | 9.4 |
| 6232 | 160 | 290 | 48 | 148.8 | 148.8 | 1520 | 1920 | 14.5 |
| 6234 | 170 | 310 | 52 | 169.6 | 179.2 | 1520 | 1920 | 17.5 |
| 6236 | 180 | 320 | 52 | 183.2 | 192 | 1440 | 1760 | 18.5 |
| 6238 | 190 | 340 | 55 | 204 | 224 | 1360 | 1600 | 23 |
| 6240 | 200 | 360 | 58 | 216 | 248 | 1360 | 1600 | 28 |
| 6244 | 220 | 400 | 65 | 236.8 | 292 | 1200 | 1440 | 37 |
| 6248 | 240 | 440 | 72 | 286.4 | 380 | 1040 | 1280 | 51 |
| 6252 | 260 | 480 | 80 | 312 | 424 | 880 | 1120 | 65.5 |
| 6256 | 280 | 500 | 80 | 338.4 | 480 | 880 | 1120 | 71 |
| 6300 | 10 | 35 | 11 | 6.448 | 2.72 | 16000 | 20800 | 0.053 |
| 6301 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 7.8 | 3.32 | 15200 | 19200 | 0.06 |
| 6302 | 15 | 42 | 13 | 9.12 | 4.32 | 13600 | 16000 | 0.082 |
| 6303 | 17 | 47 | 14 | 10.8 | 5.24 | 12800 | 15200 | 0.12 |
| 6304 | 20 | 52 | 15 | 12.72 | 6.24 | 10400 | 12800 | 0.14 |
| 6305 | 25 | 62 | 17 | 18 | 9.28 | 8800 | 11200 | 0.23 |
| 6306 | 30 | 72 | 19 | 22.48 | 12.8 | 7200 | 8800 | 0.35 |
| 6307 | 35 | 80 | 21 | 26.56 | 15.2 | 6800 | 8000 | 0.46 |
| 6308 | 40 | 90 | 23 | 32.8 | 19.2 | 6000 | 7200 | 0.63 |
| 6309 | 45 | 100 | 25 | 42.16 | 25.2 | 53600 | 6400 | 0.83 |
| 6310 | 50 | 110 | 27 | 49.44 | 30.4 | 5040 | 6000 | 1.05 |
| 6311 | 55 | 120 | 29 | 57.2 | 36 | 4480 | 5360 | 1.35 |
| 6312 | 60 | 130 | 31 | 65.52 | 41.6 | 4000 | 4800 | 1.7 |
| 6313 | 65 | 140 | 33 | 73.84 | 48 | 3840 | 4480 | 2.1 |
| 6314 | 70 | 150 | 35 | 83.2 | 54.4 | 3600 | 4240 | 2.5 |
| 6315 | 75 | 160 | 37 | 91.2 | 61.2 | 3440 | 4000 | 3 |
| 6316 | 80 | 170 | 39 | 99.2 | 69.2 | 3040 | 3600 | 3.6 |
| 6317 | 85 | 180 | 41 | 106.4 | 77.2 | 2880 | 3440 | 4.25 |
| 6318 | 90 | 190 | 43 | 114.4 | 86.4 | 2720 | 3200 | 4.9 |
| 6319 | 95 | 200 | 45 | 122.4 | 94.4 | 2560 | 3040 | 5.65 |
| 6320 | 100 | 215 | 47 | 139.2 | 112 | 2400 | 2880 | 7 |
| 6321 | 105 | 225 | 49 | 145.6 | 122.4 | 2240 | 2720 | 8.25 |
| 6322 | 110 | 240 | 50 | 162.4 | 144 | 2080 | 2560 | 9.55 |
| 6324 | 120 | 260 | 55 | 166.4 | 148.8 | 1920 | 2400 | 14.5 |
| 6326 | 130 | 280 | 58 | 183.2 | 172.8 | 1760 | 2240 | 18 |
| 6328 | 140 | 300 | 62 | 200.8 | 196 | 1600 | 2080 | 22 |
| 6330 | 150 | 320 | 65 | 220.8 | 228 | 1520 | 1920 | 26 |
| 6332 | 160 | 340 | 68 | 220.8 | 228 | 1440 | 1760 | 29 |
| 6334 | 170 | 360 | 72 | 249.6 | 272 | 1360 | 1600 | 34.5 |
| 6336 | 180 | 380 | 75 | 280.8 | 324 | 1280 | 1600 | 42.5 |
| 6338 | 190 | 400 | 78 | 296.8 | 344 | 1280 | 1520 | 49 |
| 6340 | 200 | 420 | 80 | 301.6 | 372 | 1200 | 1440 | 55.5 |
| 6344 | 220 | 460 | 88 | 328 | 416 | 1040 | 1280 | 72.5 |
Packaging & Shipping
Please contact us for more pictures of different packing.
|
Universal Packing |
Without any logo on bearings or packing. |
|
JDZ Packing |
With our brand JDZ on bearings and packing. |
|
Customized Packing |
Depends on buyer’s requirements. |
|
Original Brand Packing |
Bearing and packing are both original. Please contact us for pictures. |
QUALITY ASSURANCE
100% Quality inspection to ensure the bearings are with good quality before shipping.
Company Profile
ZheJiang CZPT Precision Bearing Co.,Ltd. was founded by ZheJiang Defa Bearing Co.,Ltd, factory is located in ZheJiang province, China.
We are a bearing manufacturer integrating the research, development and sales of bearings, with a floor area of 18,000 square meters and a plant area of 8,800 square meters. Equipped with modern production equipment and advanced detection instruments.
We can provide all types bearings and OEM service according to customers’ requirements.
Our products are widely used in the automobile, agricultural, textile production, mining, printing and packing industries, in addition to various applications at airports, in air-conditioning systems, conveying devices, ships ad so on. Our products are being exported to more than 50 countries and regions overseas including Singapore, Thailand, Iran, Turkey, Poland, Italy, England, France, Russia, Germany, the United States, Australia, Argentina, Brazil as well as other countries and regions all over the world.
We are a trusted and reliable bearing supplier, choose us to be your good partner!
Quality Inspection
Our Advantages
1. Professional production team with advanced production equipment and testing instruments.
2. Many years of export experience can provide customers with better service and problem-solving capabilities.
3. Customers all over the world enable us to better understand the market and provide customers with suitable bearings.
4. Sincerity, cooperation, mutual and provide good quality bearings for clients are the development idea of our company
5. Quick delivery, shipping goods on time. Save more time and cost for all customers.
FAQ
1. Q: Are you trading company or manufacturer ?
A: We have our own factory , our type is factory + trade.
2. Q: Could you accept OEM and customize?
A: Yes, we can customize products according to your sample or drawing.
3. Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: If stock, within 7 days to ship or based on your order quantity.
4. Q: Could you supply sample for free?
A: Yes, we can offer the sample for free,do you mind to buy a “ticket” for her?
More details, please contact with us. Thanks for your time!
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Bearing Type: | Deep Groove Ball Bearing |
|---|---|
| Precision Rating: | P0 P6 P5 P4 P2 or ABEC1 ABEC3 ABEC5 ABEC7 ABEC9 |
| Bearing Clearance: | C0/C3/C4 |
| Vibration: | Z1V1, Z2V2, Z3V3; Z4V4 |
| Seals Type: | Zz 2RS Open |
| Hardness: | 58-62 HRC |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can you Provide Examples of Industries where Ball Bearings are Crucial Components?
Ball bearings are essential components in a wide range of industries where smooth motion, load support, and precision are vital. Here are some examples of industries where ball bearings play a crucial role:
- Automotive Industry:
Ball bearings are used in various automotive applications, including wheel hubs, transmissions, engines, steering systems, and suspension components. They provide reliable rotation and support in both passenger vehicles and commercial vehicles.
- Aerospace Industry:
In the aerospace sector, ball bearings are found in aircraft engines, landing gear systems, control surfaces, and avionics equipment. Their ability to handle high speeds and precision is vital for aviation safety.
- Industrial Machinery:
Ball bearings are integral to a wide range of industrial machinery, including pumps, compressors, conveyors, machine tools, printing presses, and textile machinery. They facilitate smooth operation and load distribution in these diverse applications.
- Medical Equipment:
In medical devices and equipment, ball bearings are used in surgical instruments, imaging equipment, dental tools, and laboratory machinery. Their precision and smooth movement are crucial for accurate diagnostics and treatments.
- Robotics and Automation:
Ball bearings are key components in robotic arms, automation systems, and manufacturing machinery. They enable precise movement, high-speed operation, and reliable performance in automated processes.
- Renewable Energy:
Wind turbines and solar tracking systems utilize ball bearings to enable efficient rotation and tracking of the wind blades and solar panels. Ball bearings withstand the dynamic loads and environmental conditions in renewable energy applications.
- Marine and Shipbuilding:
Ball bearings are used in marine applications such as ship propulsion systems, steering mechanisms, and marine pumps. They withstand the corrosive environment and provide reliable performance in maritime operations.
- Heavy Equipment and Construction:
In construction machinery like excavators, bulldozers, and cranes, ball bearings support the movement of heavy loads and enable efficient operation in demanding environments.
- Electronics and Consumer Appliances:
Consumer electronics like electric motors, computer hard drives, and household appliances rely on ball bearings for smooth motion and reliable operation.
- Oil and Gas Industry:
In oil and gas exploration and extraction equipment, ball bearings are used in drilling rigs, pumps, and processing machinery. They handle the high loads and harsh conditions of this industry.
These examples demonstrate how ball bearings are indispensable components in various industries, contributing to the efficiency, reliability, and functionality of diverse mechanical systems and equipment.

How do Ceramic Ball Bearings Compare to Traditional Steel Ball Bearings in Terms of Performance?
Ceramic ball bearings and traditional steel ball bearings have distinct characteristics that can impact their performance in various applications. Here’s a comparison of how these two types of bearings differ in terms of performance:
- Material Composition:
Ceramic Ball Bearings:
Ceramic ball bearings use ceramic rolling elements, typically made from materials like silicon nitride (Si3N4) or zirconium dioxide (ZrO2). These ceramics are known for their high hardness, low density, and resistance to corrosion and wear.
Traditional Steel Ball Bearings:
Traditional steel ball bearings use steel rolling elements. The type of steel used can vary, but common materials include chrome steel (52100) and stainless steel (440C). Steel bearings are known for their durability and strength.
- Friction and Heat:
Ceramic Ball Bearings:
Ceramic bearings have lower friction coefficients compared to steel bearings. This results in reduced heat generation during operation, contributing to higher efficiency and potential energy savings.
Traditional Steel Ball Bearings:
Steel bearings can generate more heat due to higher friction coefficients. This can lead to increased energy consumption in applications where efficiency is crucial.
- Weight:
Ceramic Ball Bearings:
Ceramic bearings are lighter than steel bearings due to the lower density of ceramics. This weight reduction can be advantageous in applications where minimizing weight is important.
Traditional Steel Ball Bearings:
Steel bearings are heavier than ceramic bearings due to the higher density of steel. This weight may not be as critical in all applications but could impact overall equipment weight and portability.
- Corrosion Resistance:
Ceramic Ball Bearings:
Ceramic bearings have excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for applications in corrosive environments, such as marine or chemical industries.
Traditional Steel Ball Bearings:
Steel bearings are susceptible to corrosion, especially in harsh environments. Stainless steel variants offer improved corrosion resistance but may still corrode over time.
- Speed and Precision:
Ceramic Ball Bearings:
Ceramic bearings can operate at higher speeds due to their lower friction and ability to withstand higher temperatures. They are also known for their high precision and low levels of thermal expansion.
Traditional Steel Ball Bearings:
Steel bearings can operate at high speeds as well, but their heat generation may limit performance in certain applications. Precision steel bearings are also available but may have slightly different characteristics compared to ceramics.
- Cost:
Ceramic Ball Bearings:
Ceramic bearings are generally more expensive to manufacture than steel bearings due to the cost of ceramic materials and the challenges in producing precision ceramic components.
Traditional Steel Ball Bearings:
Steel bearings are often more cost-effective to manufacture, making them a more economical choice for many applications.
In conclusion, ceramic ball bearings and traditional steel ball bearings offer different performance characteristics. Ceramic bearings excel in terms of low friction, heat generation, corrosion resistance, and weight reduction. Steel bearings are durable, cost-effective, and widely used in various applications. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as speed, precision, corrosion resistance, and budget considerations.

What are the Different Components that Make up a Typical Ball Bearing?
A typical ball bearing consists of several essential components that work together to reduce friction and support loads. Here are the main components that make up a ball bearing:
- Outer Ring:
The outer ring is the stationary part of the bearing that provides support and houses the other components. It contains raceways (grooves) that guide the balls’ movement.
- Inner Ring:
The inner ring is the rotating part of the bearing that attaches to the shaft. It also contains raceways that correspond to those on the outer ring, allowing the balls to roll smoothly.
- Balls:
The spherical balls are the rolling elements that reduce friction between the inner and outer rings. Their smooth rolling motion enables efficient movement and load distribution.
- Cage or Retainer:
The cage, also known as the retainer, maintains a consistent spacing between the balls. It prevents the balls from touching each other, reducing friction and preventing jamming.
- Seals and Shields:
Many ball bearings include seals or shields to protect the internal components from contaminants and retain lubrication. Seals provide better protection against contaminants, while shields offer less resistance to rotation.
- Lubricant:
Lubrication is essential to reduce friction, wear, and heat generation. Bearings are typically filled with lubricants that ensure smooth movement between the balls and raceways.
- Flanges and Snap Rings:
In some designs, flanges or snap rings are added to help position and secure the bearing in its housing or on the shaft. Flanges prevent axial movement, while snap rings secure the bearing radially.
- Raceways:
Raceways are the grooved tracks on the inner and outer rings where the balls roll. The shape and design of the raceways influence the bearing’s load-carrying capacity and performance.
- Anti-Friction Shield:
In certain high-speed applications, a thin anti-friction shield can be placed between the inner and outer rings to minimize friction and heat generation.
These components work together to enable the smooth rolling motion, load support, and reduced friction that characterize ball bearings. The proper design and assembly of these components ensure the bearing’s optimal performance and longevity in various applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China Hot selling Motorcycle Spare Part Rolling Radial Deep Groove Ball Bearing 6302 bearing distributors
Product Description
Product Parameters
| Model | Category | RTS/Custom | Size(mm) d*D*H (mm) |
Precision grade | Seal Type | Number of Row | Application |
| 6302 | Deep Groove Ball Bearing | RTS | 15*42*13mm | P0 P2 P4 P5 P6 | OPEN ZZ 2RS RS | Single | Machinery |
| Material | Material of Balls | Lubrication | Vibration | Clearance | Hardness | Deliery Time | Packing |
| Chrome Steel GCr15 | Chrome Steel GCr15 | Grease or Oil | Standard Vibration Z1/Z2/Z3/Z4/V1/V2/V3/V4 |
Standard Clearance C0/C2/C3/C4/C5 |
HRC60-65 | <=50000,3 <=100000,5 |
Single Box+Cartons+Pallet |
Product Description
Detailed Photos
Our business:Produce and customize various bearing brands. (Packaging and logo can be customized. All copyright belongs to the customer. We promise not to disclose any information.)
Product Series
| Bearing type | Boundary Dimensions( mm ) | Speed Rating(ipm) | Load Rating(kn) | Weight(kg) | ||||
| d | D | B | Grease lubrication | Oil lubrication | Dynamic Cr | Static Cor | ||
| 6300 | 10 | 35 | 11 | 18000 | 24000 | 7.65 | 3.48 | 0.053 |
| 6301 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 17000 | 22000 | 9.72 | 5.08 | 0.06 |
| 6302 | 15 | 42 | 13 | 16000 | 20000 | 11.5 | 5.42 | 0.082 |
| 6303 | 17 | 47 | 14 | 15000 | 18000 | 13.5 | 6.58 | 0.115 |
| 6304 | 20 | 52 | 15 | 13000 | 16000 | 15.8 | 7.88 | 0.142 |
| 6305 | 25 | 62 | 17 | 11000 | 13000 | 20.6 | 11.3 | 0.232 |
| 6306 | 30 | 72 | 19 | 6600 | 12000 | 26.7 | 15 | 0.346 |
| 6307 | 35 | 80 | 21 | 8500 | 10000 | 33.4 | 19.3 | 0.457 |
| 6308 | 40 | 90 | 23 | 7000 | 8500 | 40.8 | 24 | 0.639 |
| 6309 | 45 | 100 | 25 | 6300 | 7500 | 52.8 | 31.8 | 0.837 |
| 6310 | 50 | 110 | 27 | 6300 | 7500 | 62 | 38 | 1.07 |
| 6311 | 55 | 120 | 29 | 5600 | 6700 | 71.5 | 45 | 1.39 |
| 6312 | 60 | 130 | 31 | 5300 | 6300 | 82 | 48.5 | 1.71 |
| 6313 | 65 | 140 | 33 | 4800 | 5600 | 92.5 | 59.5 | 2.1 |
| 6314 | 70 | 150 | 35 | 4500 | 5300 | 104 | 68 | 2.55 |
| 6315 | 75 | 160 | 37 | 4300 | 5000 | 113 | 116 | 3.1 |
| 6316 | 80 | 170 | 39 | 3800 | 4500 | 119 | 86.5 | 3.64 |
| 6317 | 85 | 180 | 41 | 3800 | 4500 | 102 | 96.5 | 4.33 |
| 6318 | 90 | 190 | 43 | 3400 | 4000 | 144 | 108 | 4.97 |
| 6319 | 95 | 200 | 45 | 3200 | 3800 | 152 | 122 | 5.65 |
| 6320 | 100 | 215 | 47 | 2800 | 3600 | 173 | 140 | 7.09 |
| 6321 | 105 | 225 | 49 | 2600 | 3200 | 184 | 153 | 8.05 |
| 6322 | 110 | 240 | 50 | 2400 | 3000 | 205 | 178 | 9.53 |
| 6324 | 120 | 260 | 55 | 2200 | 2800 | 228 | 208 | 12.2 |
| 6326 | 130 | 280 | 58 | 2000 | 2600 | 253 | 242 | 14.77 |
| 6328 | 140 | 300 | 62 | 1900 | 2400 | 275 | 272 | 18.33 |
| 6330 | 150 | 320 | 65 | 1700 | 2200 | 288 | 295 | 21.87 |
| 6332 | 160 | 340 | 68 | 1600 | 2000 | 313 | 340 | 26.43 |
| 6334 | 170 | 360 | 72 | 1500 | 1900 | 335 | 378 | 31.14 |
| 6336 | 180 | 380 | 75 | 1400 | 1800 | 358 | 396 | 35.23 |
| 6338 | 190 | 400 | 78 | 1300 | 1700 | 379 | 438 | 39.45 |
| 6340 | 200 | 420 | 80 | 1200 | 1600 | 391 | 496 | 46.89 |
| 6344 | 220 | 460 | 88 | 1100 | 1500 | 410 | 520 | 52.45 |
| 6348 | 240 | 500 | 95 | 1000 | 1400 | 442 | 585 | 59.46 |
| 6352 | 260 | 540 | 102 | 900 | 1300 | 507 | 710 | 64.23 |
| 6356 | 280 | 580 | 108 | 800 | 1200 | 572 | 850 | 73.67 |
| 6360 | 300 | 620 | 109 | 700 | 1100 | 590 | 920 | 85.34 |
Type Of Deep Groove Ball Bearing
1. Deep Groove Ball Bearing With Dust Cover
Generally Used In The Single Lubrication Is More Difficult, The Placement Of Lubricating Oil And Check The Lubrication Is Not Convenient Conditions, Usually Injected Into The Bearing Rust, Lubrication Dual-Purpose Lithium Grease Is 1/4 To 1/3 Of The Bearing Internal Space.
2. Deep Groove Ball Bearing With Sealing Ring
Its Performance, Grease Filling, Use And Bearing With Dust Cover Are Basically The Same, The Difference Is That There Is A Large Gap Between The Dust Cover And The Inner Ring, And The Sealing Lip And The Inner Ring Of The Non-Contact Seal Ring Is Small, There Is No Gap Between The Sealing Lip And The Inner Ring Of The Contact Seal Ring Bearing, The Sealing Effect Is Good, But The Friction Coefficient Has Increased.
3, There Are Stop Groove And Deep Groove Ball Bearings With Stop Ring
In Addition To The Function Of Bearing Radial Load, The Deep Groove Ball Bearing With The Stop Ring Can Also Limit The Axial Displacement Of The Bearing, Simplify The Structure Of The Bearing Seat And Reduce The Bearing Size. Generally Used In Cars, Tractors And Other Axial Load Is Not Large Working Parts.
4. Deep Groove Ball Bearing With Ball Filling Gap
There Are Notches In The Inner And Outer Rings On One Side, From Which More Balls Can Be Loaded, Increasing Its Radial Load Capacity. However, Due To The Small Axial Load Capacity, It Can Not Run At High Speed. If There Is A Large Axial Load, It Needs To Be Used With The General Deep Groove Ball Bearing.
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
Exhibitions&Partners
FAQ
Q:Are you trading company or manufacturer?
–We are the company dealing in trading business and manufacturing business.
Q:What’s the MOQ?
–MOQ is 2pcs for standardized products; 300pcs for customized products. There is no MOQ for sample orders.
Q:How long is the lead time?
–The lead time for sample orders is 1-3 days, for bulk orders is generally in 3-15 days.The delivery time is generally in 2 days after payment. It’s according to the order amount.
Q:Do you offer free samples?
–If you place an order, we can return part of sample fee even all of fee to you. It also depends on the quantity of order and the type of sample. And you just need to pay freight.
Q: Could you customized for me?
–Sure,we can supply OEM service as per your drawing or samples.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Chrome Steel Gcr15 |
|---|---|
| Bearing Type: | 6302 |
| Category: | Deep Groove Ball Bearing |
| Seal Type: | Open Zz 2RS RS |
| Number of Row: | Single |
| Weight: | 0.082kg |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the Common Signs of Wear or Damage in Ball Bearings that Indicate the Need for Replacement?
Ball bearings are subjected to wear and stress during operation, and over time, they may exhibit signs of damage or deterioration that warrant replacement. Recognizing these signs is crucial to prevent catastrophic failure and ensure safe and reliable operation. Here are the common signs of wear or damage in ball bearings:
- Unusual Noise:
If you hear unusual grinding, clicking, or rumbling noises coming from the bearing during operation, it may indicate worn-out or damaged components. Unusual noise suggests that the bearing is no longer operating smoothly.
- Vibration:
Excessive vibration in the machinery can be a sign of bearing wear. Vibrations can result from uneven wear, misalignment, or damaged components within the bearing.
- Increased Temperature:
Higher operating temperatures than usual may indicate increased friction due to inadequate lubrication, wear, or other issues. Monitoring the bearing’s temperature can help identify potential problems.
- Irregular Movement:
If you notice irregular movement, jerking, or sticking during rotation, it could be a sign that the bearing is no longer operating smoothly. This may be due to damaged rolling elements or raceways.
- Reduced Performance:
If the machinery’s performance has decreased, it may be due to a compromised bearing. Reduced efficiency, increased energy consumption, or a decline in overall performance could be indicators of bearing wear.
- Visible Wear or Damage:
Inspect the bearing for visible signs of wear, such as pitting, scoring, or discoloration on the rolling elements or raceways. Severe wear or damage is a clear indication that the bearing needs replacement.
- Leakage or Contamination:
If there is evidence of lubricant leakage, contamination, or the presence of foreign particles around the bearing, it suggests that the seal or shield may be compromised, leading to potential damage.
- Looseness or Excessive Play:
If you can feel excessive play or looseness when manually moving the bearing, it could indicate worn-out components or misalignment.
- Reduced Lifespan:
If the bearing’s expected lifespan is significantly shorter than usual, it may be due to inadequate lubrication, excessive loads, or improper installation, leading to accelerated wear.
- Frequent Failures:
If the bearing is consistently failing despite regular maintenance and proper use, it could indicate a chronic issue that requires addressing, such as inadequate lubrication or misalignment.
It’s important to conduct regular inspections, monitor performance, and address any signs of wear or damage promptly. Replacing worn or damaged ball bearings in a timely manner can prevent further damage to machinery, reduce downtime, and ensure safe and efficient operation.

How do Temperature and Environmental Conditions Affect the Performance of Ball Bearings?
Temperature and environmental conditions have a significant impact on the performance and longevity of ball bearings. The operating environment can influence factors such as lubrication effectiveness, material properties, and overall bearing behavior. Here’s how temperature and environmental conditions affect ball bearing performance:
- Lubrication:
Temperature variations can affect the viscosity and flow characteristics of lubricants. Extreme temperatures can cause lubricants to become too thin or too thick, leading to inadequate lubrication and increased friction. In high-temperature environments, lubricants can degrade, reducing their effectiveness.
- Material Properties:
Temperature changes can alter the material properties of the bearing components. High temperatures can lead to thermal expansion, affecting bearing clearances and potentially causing interference between components. Extreme cold temperatures can make materials more brittle and prone to fracture.
- Clearance Changes:
Temperature fluctuations can cause changes in the internal clearance of ball bearings. For instance, at high temperatures, materials expand, leading to increased clearance. This can affect bearing performance, load distribution, and overall stability.
- Corrosion and Contamination:
Harsh environmental conditions, such as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or abrasive particles, can lead to corrosion and contamination of bearing components. Corrosion weakens the material, while contamination accelerates wear and reduces bearing life.
- Thermal Stress:
Rapid temperature changes can result in thermal stress within the bearing components. Differential expansion and contraction between the inner and outer rings can lead to stress and distortion, affecting precision and bearing integrity.
- Noise and Vibration:
Temperature-related changes in material properties and internal clearances can influence noise and vibration levels. Extreme temperatures can lead to increased noise generation and vibration, affecting the overall operation of machinery.
- Lubricant Degradation:
Environmental factors like humidity, dust, and contaminants can lead to premature lubricant degradation. Oxidation, moisture absorption, and the presence of foreign particles can compromise the lubricant’s performance and contribute to increased friction and wear.
- Seal Effectiveness:
Seals and shields that protect bearings from contaminants can be affected by temperature fluctuations. Extreme temperatures can lead to seal hardening, cracking, or deformation, compromising their effectiveness in preventing contamination.
- Choosing Appropriate Bearings:
When selecting ball bearings for specific applications, engineers must consider the expected temperature and environmental conditions. High-temperature bearings, bearings with specialized coatings, and those with enhanced sealing mechanisms may be necessary to ensure reliable performance.
Overall, understanding the impact of temperature and environmental conditions on ball bearing performance is crucial for proper bearing selection, maintenance, and ensuring optimal operation in diverse industries and applications.

What are the Different Components that Make up a Typical Ball Bearing?
A typical ball bearing consists of several essential components that work together to reduce friction and support loads. Here are the main components that make up a ball bearing:
- Outer Ring:
The outer ring is the stationary part of the bearing that provides support and houses the other components. It contains raceways (grooves) that guide the balls’ movement.
- Inner Ring:
The inner ring is the rotating part of the bearing that attaches to the shaft. It also contains raceways that correspond to those on the outer ring, allowing the balls to roll smoothly.
- Balls:
The spherical balls are the rolling elements that reduce friction between the inner and outer rings. Their smooth rolling motion enables efficient movement and load distribution.
- Cage or Retainer:
The cage, also known as the retainer, maintains a consistent spacing between the balls. It prevents the balls from touching each other, reducing friction and preventing jamming.
- Seals and Shields:
Many ball bearings include seals or shields to protect the internal components from contaminants and retain lubrication. Seals provide better protection against contaminants, while shields offer less resistance to rotation.
- Lubricant:
Lubrication is essential to reduce friction, wear, and heat generation. Bearings are typically filled with lubricants that ensure smooth movement between the balls and raceways.
- Flanges and Snap Rings:
In some designs, flanges or snap rings are added to help position and secure the bearing in its housing or on the shaft. Flanges prevent axial movement, while snap rings secure the bearing radially.
- Raceways:
Raceways are the grooved tracks on the inner and outer rings where the balls roll. The shape and design of the raceways influence the bearing’s load-carrying capacity and performance.
- Anti-Friction Shield:
In certain high-speed applications, a thin anti-friction shield can be placed between the inner and outer rings to minimize friction and heat generation.
These components work together to enable the smooth rolling motion, load support, and reduced friction that characterize ball bearings. The proper design and assembly of these components ensure the bearing’s optimal performance and longevity in various applications.


editor by CX 2024-05-10
China factory Deep Groove Ball Bearing 6008 6009 6010 Motor Auto Parts Pump Bearing bearing driver
Product Description
Product Parameters
| Bearing NO | Dimensions ( mm) | Speed rating (IPM) | Basic load rating (KN) | Weight (kg) |
||||
| d | D | B | Grease | Oil | Cr | Cor | ||
| 6007 | 35 | 62 | 14 | 12000 | 14000 | 16 | 10.3 | 0.16 |
| 6007-Z | 35 | 62 | 14 | 12000 | 14000 | 16 | 10.3 | 0.16 |
| 6007-2Z | 35 | 62 | 14 | 12000 | 14000 | 16 | 10.3 | 0.16 |
| 6007-RS | 35 | 62 | 14 | 12000 | 14000 | 16 | 10.3 | 0.16 |
| 6007-2RS | 35 | 62 | 14 | 12000 | 14000 | 16 | 10.3 | 0.16 |
| 6008 | 40 | 68 | 15 | 9000 | 11000 | 15.34 | 10.85 | 0.18 |
| 6008-Z | 40 | 68 | 15 | 9000 | 11000 | 15.34 | 10.85 | 0.18 |
| 6008-2Z | 40 | 68 | 15 | 9000 | 11000 | 15.34 | 10.85 | 0.18 |
| 6008-RS | 40 | 68 | 15 | 9000 | 11000 | 15.34 | 10.85 | 0.18 |
| 6008-2RS | 40 | 68 | 15 | 9000 | 11000 | 15.34 | 10.85 | 18 |
| 6009 | 45 | 75 | 16 | 8000 | 11000 | 21.19 | 14.77 | 0.24 |
| 6009-Z | 45 | 75 | 16 | 8000 | 10000 | 21.19 | 14.77 | 0.24 |
| 6009-22 | 45 | 75 | 16 | 8000 | 10000 | 21.19 | 14.77 | 0.24 |
| 6008-RS | 45 | 75 | 16 | 8000 | 10000 | 21.19 | 14.77 | 0.24 |
| 6009-2RS | 45 | 75 | 16 | 8000 | 10000 | 21.19 | 14.77 | 0.24 |
| 6009MA | 45 | 75 | 16 | 8000 | 10000 | 20.59 | 15.26 | 0.29 |
| 6571 | 50 | 80 | 16 | 7300 | 9200 | 22.05 | 46.21 | 0.26 |
| 6571N | 50 | 80 | 16 | 7300 | 9200 | 22.05 | 16.21 | 0.26 |
| 6571-Z | 50 | 80 | 16 | 7300 | 9200 | 22.05 | 16.21 | 0.26 |
| 6571-2Z | 50 | 80 | 16 | 7300 | 9200 | 22.05 | 16.21 | 0.26 |
Detailed Photos
Product Details
1.High load capacity: Deep groove ball bearings are uniquely designed to withstand large radial and axial loads.
2.Wide applicability: widely used in motors, automobiles, construction machinery, agricultural equipment and other fields.
3.High-speed operation: It is suitable for high-speed operation environment and has good stability and working performance.
4.Low noise: Using high-quality materials and precision processing, it operates smoothly and has very low noise.
5.Dust-proof seal: Some models are equipped with rubber sealing rings, which can effectively prevent the bearing and foreign matter from entering the inside of the bearing and extend the service life.
Product Application
Motor
Automobile transmission system
Construction machinery
Agricultural equipment
Mining equipment
Other machinery and equipment
Packaging & Shipping
|
Universal Packing |
Without any logo on bearings or packing. |
|
SDLB Packing |
With our brand SDLB on bearings and packing. |
|
Customized Packing |
Depends on buyer’s requirements. |
|
Original Brand Packing |
Bearing and packing are both original. Please contact us for pictures. |
Certifications
Other Bearings
We supply different types of ball and roller bearings,tapered roller bearing, deep groove ball bearing, spherical roller bearing, Linear guides.
FAQ
Q1: What is our advantages?
A: Manufacturer – Do it only with the Best;Your Choice make different.
Q2: Our Products
A: Equal-section thin-wall bearings,Linear CZPT bearings,Deep groove ball bearing,Cylindrical roller bearing,Spherical roller bearing,Needle roller bearing,Angular contact ball bearing,Tapered roller bearing,Thrust ball bearing,Self-aligning ball bearing.
Q3: Process of our production
A: Heat Treatment – Grinding – Parts Inspection – Assembly – Final Inspection – Packing
Q4: How to customize bearing(non-standard) from your company?
A: We offer OEM,Customized(Non-standard) service and you need to provide drawing and detailed Technical Data.
Q5: What should I care before installation?
A: Normally, the preservative with which new bearings are coated before leaving the factory does not need to be removed; it is only necessary to wipe off the outside cylindrical surface and bore, if the grease is not compatible with the preservative, it is necessary to wash and carefully dry the bearing.Bearings should be installed in a dry, dust-free room away from metal working or other machines producing swarf and dust.
Q6: How to stock and maintenance my bearings right?
A: Do not store bearings directly on concrete floors, where water can condense and collect on the bearing;Store the bearings on a pallet or shelf, in an area where the bearings will not be subjected to high humidity or sudden and severe temperature changes that may result in condensation forming;Always put oiled paper or, if not available, plastic sheets between rollers and cup races of tapered roller bearings.
To get price list of promotion bearings, please contact us.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Precision Rating: | P0 P4 P5 P6 |
|---|---|
| Number of Row: | Single Row |
| Stability: | High |
| Width: | 16 mm |
| Weight: | 0.26 Kg |
| Radial Clearance: | C2 Co C3 C4 C5 |
| Samples: |
US$ 15/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What are the Materials Typically Used in Manufacturing Ball Bearings and Their Advantages?
Ball bearings are manufactured using a variety of materials, each chosen for its specific properties and advantages in various applications. Here are some commonly used materials in ball bearing manufacturing and their respective benefits:
- High-Carbon Chrome Steel (AISI 52100):
This is the most common material used for ball bearing manufacturing. It offers excellent hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue strength. High-carbon chrome steel bearings are suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial machinery to automotive components.
- Stainless Steel (AISI 440C, AISI 304, AISI 316):
Stainless steel bearings are corrosion-resistant and suitable for applications where moisture, chemicals, or exposure to harsh environments are concerns. AISI 440C offers high hardness and corrosion resistance, while AISI 304 and AISI 316 provide good corrosion resistance and are often used in food and medical industries.
- Ceramic:
Ceramic bearings use silicon nitride (Si3N4) or zirconia (ZrO2) balls. Ceramic materials offer high stiffness, low density, and excellent resistance to corrosion and heat. Ceramic bearings are commonly used in high-speed and high-temperature applications, such as in aerospace and racing industries.
- Plastic (Polyamide, PEEK):
Plastic bearings are lightweight and offer good corrosion resistance. Polyamide bearings are commonly used due to their low friction and wear properties. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) bearings provide high-temperature resistance and are suitable for demanding environments.
- Bronze:
Bronze bearings are often used in applications where self-lubrication is required. Bronze has good thermal conductivity and wear resistance. Bearings made from bronze are commonly used in machinery requiring frequent starts and stops.
- Hybrid Bearings:
Hybrid bearings combine steel rings with ceramic balls. These bearings offer a balance between the advantages of both materials, such as improved stiffness and reduced weight. Hybrid bearings are used in applications where high speeds and low friction are essential.
- Specialty Alloys:
For specific applications, specialty alloys may be used to meet unique requirements. For example, bearings used in extreme temperatures or corrosive environments may be made from materials like titanium or hastelloy.
- Coated Bearings:
Bearings may also be coated with thin layers of materials like diamond-like carbon (DLC) or other coatings to enhance performance, reduce friction, and improve wear resistance.
The choice of material depends on factors such as application requirements, operating conditions, load, speed, and environmental factors. Selecting the right material is essential for ensuring optimal bearing performance, longevity, and reliability in diverse industries and applications.

Are there any Industry Standards or Certifications that Ball Bearings should Meet?
Yes, there are several industry standards and certifications that ball bearings should meet to ensure their quality, performance, and reliability. These standards help manufacturers, engineers, and customers assess the suitability of bearings for specific applications. Some of the key standards and certifications for ball bearings include:
- ISO Standards:
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed a series of standards related to ball bearings. ISO 15 defines dimensions, boundary dimensions, and tolerances for radial bearings. ISO 281 specifies dynamic load ratings and calculation methods for bearings’ life calculations.
- ABEC (Annular Bearing Engineering Committee) Ratings:
ABEC ratings are commonly used in North America to indicate the precision and performance of ball bearings. Ratings range from ABEC 1 (lowest precision) to ABEC 9 (highest precision). However, it’s important to note that ABEC ratings focus primarily on dimensional tolerances and do not encompass all aspects of bearing quality.
- DIN Standards:
The German Institute for Standardization (Deutsches Institut für Normung, DIN) has published various standards related to ball bearings. DIN 625 covers dimensions for deep groove ball bearings, while DIN 616 provides guidelines for precision angular contact ball bearings.
- JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards):
JIS standards are used in Japan and internationally to define the characteristics and dimensions of various products, including ball bearings. JIS B 1512 outlines the classification and dimensions of rolling bearings.
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) Standards:
ASTM has standards that cover various aspects of bearing testing, performance, and materials. ASTM F2215, for instance, specifies the requirements for ball bearings used in surgical implants.
- CE Marking:
CE marking indicates that a product complies with European Union health, safety, and environmental requirements. It may be required for bearings used in machinery intended to be sold within the EU market.
- Industry-Specific Standards:
Various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and nuclear, have specific standards or certifications that bearings must meet to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with industry-specific requirements.
- Quality Management Systems:
Manufacturers that adhere to quality management systems, such as ISO 9001, demonstrate their commitment to consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. Certification to these systems indicates that the manufacturing process follows established protocols and best practices.
When selecting ball bearings, it’s important to consider the relevant standards and certifications that align with the application’s requirements. This ensures that the bearings meet recognized quality and performance criteria, ultimately contributing to reliable and efficient operation.

What Factors should be Considered when Selecting a Ball Bearing for a Particular Application?
Selecting the right ball bearing for a specific application involves careful consideration of various factors to ensure optimal performance, longevity, and reliability. Here are the key factors that should be taken into account:
- Load Type and Magnitude:
Determine the type of load (radial, axial, or combined) and the magnitude of the load that the bearing will need to support. Choose a bearing with the appropriate load-carrying capacity to ensure reliable operation.
- Speed and Operating Conditions:
Consider the rotational speed of the application and the operating conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants. Different bearing types and materials are suited for varying speeds and environments.
- Accuracy and Precision:
For applications requiring high accuracy and precision, such as machine tool spindles or optical instruments, choose high-precision bearings that can maintain tight tolerances and minimize runout.
- Space Limitations:
If the application has limited space, choose miniature or compact ball bearings that can fit within the available dimensions without compromising performance.
- Thrust and Radial Loads:
Determine whether the application requires predominantly thrust or radial load support. Choose the appropriate type of ball bearing (thrust, radial, or angular contact) based on the primary load direction.
- Alignment and Misalignment:
If the application experiences misalignment between the shaft and housing, consider self-aligning ball bearings that can accommodate angular misalignment.
- Mounting and Installation:
Consider the ease of mounting and dismounting the bearing. Some applications may benefit from features like flanges or snap rings for secure installation.
- Lubrication and Maintenance:
Choose a bearing with appropriate lubrication options based on the application’s speed and temperature range. Consider whether seals or shields are necessary to protect the bearing from contaminants.
- Environmental Conditions:
Factor in the operating environment, including exposure to corrosive substances, chemicals, water, or dust. Choose materials and coatings that can withstand the specific environmental challenges.
- Bearing Material:
Select a bearing material that suits the application’s requirements. Common materials include stainless steel for corrosion resistance and high-carbon chrome steel for general applications.
- Bearing Arrangement:
Consider whether a single-row, double-row, or multiple bearings in a specific arrangement are needed to accommodate the loads and moments present in the application.
By carefully evaluating these factors, engineers and designers can choose the most suitable ball bearing that aligns with the specific demands of the application, ensuring optimal performance, durability, and overall operational efficiency.


editor by CX 2024-05-10